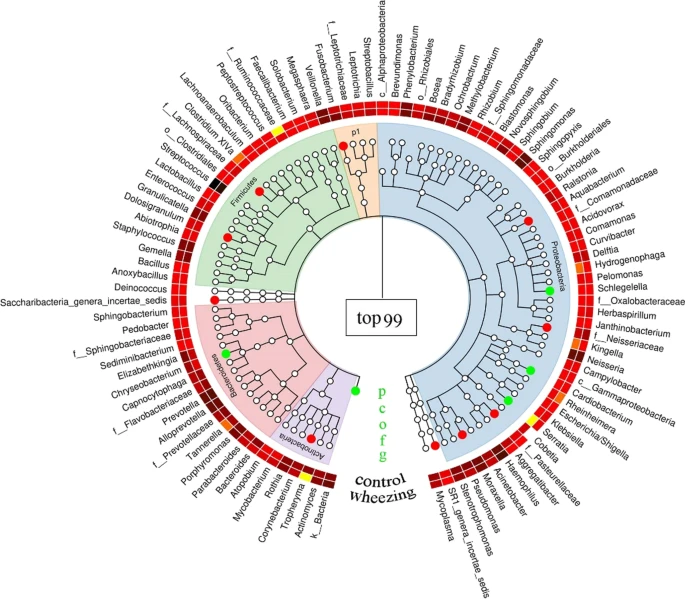
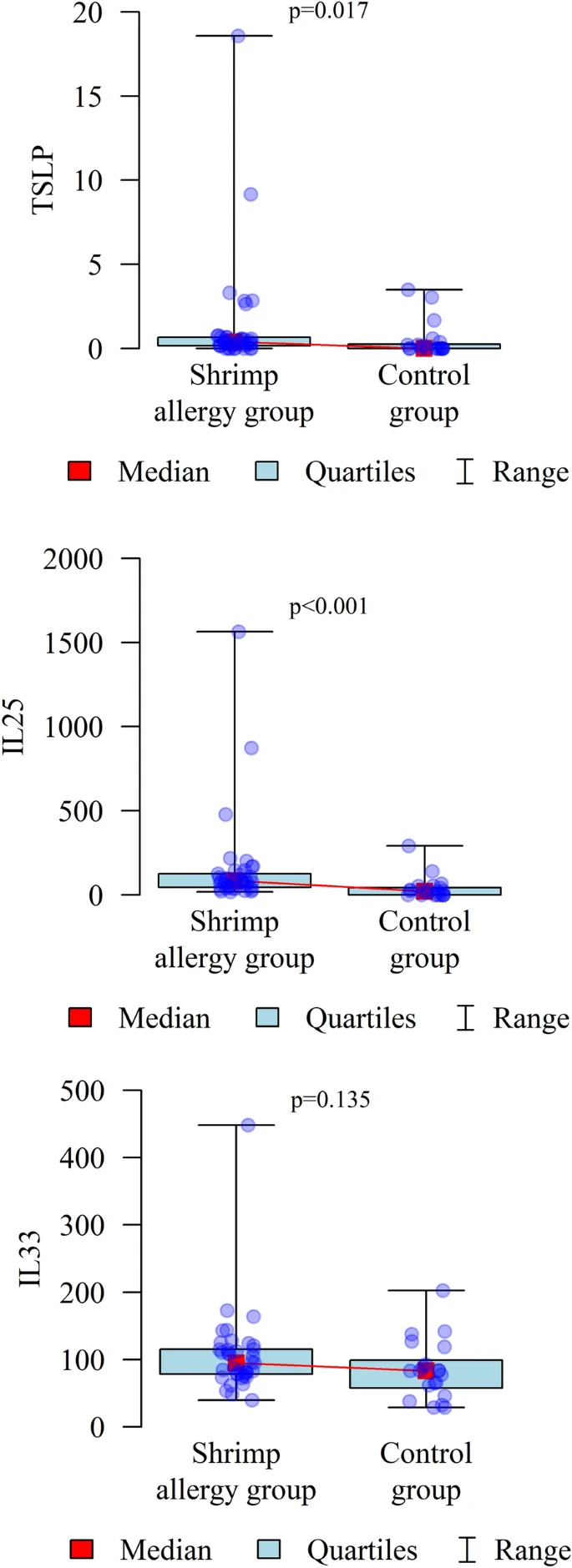
- Research
- Open Access
M. Tomchaney, M. Contoli, J. Mayo, S. Baraldo, S. Li, C. R. Cabel, D. A. Bull, S. Lick, J. Malo, S. Knoper, S. S. Kim, J. Tram, J. Rojas-Quintero, M. Kraft, J. G. Ledford, Y. Tesfaigzi, F. D. Martinez, C. A. Thorne, F. Kheradmand, S. K. Campos, A. Papi & F. Polverino
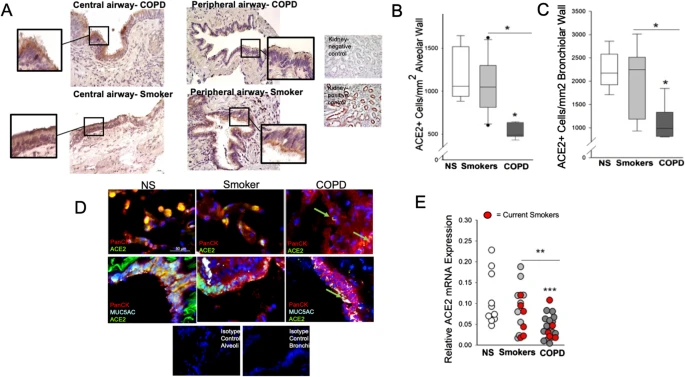
How cigarette smoke (CS) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affect severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) infection and severity is controversial. We investigated the effects of COPD and CS on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2 in vivo in COPD patients and controls and in CS-exposed mice, and the effects of CS on SARS-CoV-2 infection in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro.