Research Open Access
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
December 13, 2022
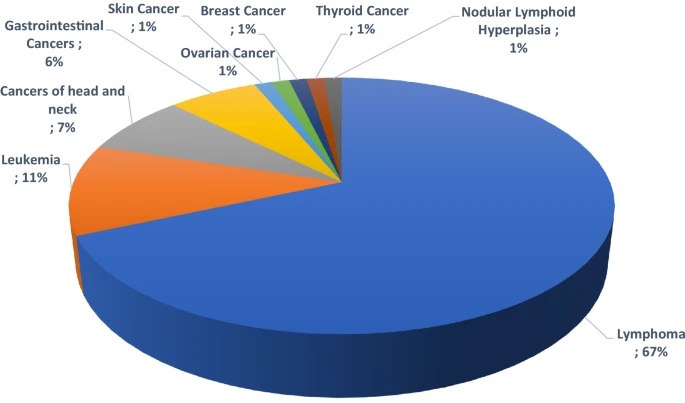
Diversity of malignancies in patients with different types of inborn errors of immunity
December 9, 2022
International recommendations on epinephrine auto-injector doses often differ from standard weight-based guidance: a review and clinical proposals
Abstract
Background
In anaphylaxis, the dosing of injectable epinephrine in medical settings has been arbitrarily recommended to be 0.01 mg/kg of body weight. For ethical reasons, there have been no dose–response studies or double-blind studies performed on patients with active anaphylaxis. Intramuscular delivery of epinephrine has been the standard. Auto-injectors for use in the treatment of anaphylaxis are available in four strengths (0.1, 0.15, 0.3, and 0.5 mg). However, in many countries, only the 0.15 and 0.3 mg strengths are available. Consequently, many adult, heavy patients are prescribed the 0.3 mg dose, which may result in only one-fifth to one-third of the recommended weight-based dose being administered in heavy patients experiencing anaphylaxis. Underdosing may have therefore contributed to mortality in anaphylaxis.
Associations between food allergy, country of residence, and healthcare access
- Letter to the Editor
- Open Access
- Kaitlyn A. Merrill,
- Elissa M. Abrams,
- Sara V. Good,
- Ruchi S. Gupta,
- Carina Venter,
- Tara Lynn M. Frykas,
- Michael A. Golding &
- Jennifer L. P. Protudjer
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 18, Article number: 103 (2022)
Abstract
Background
To date, little consideration has been given to access to allergy-related care, despite the fact that food allergy affects a considerable proportion of children. As such, the current study aimed to describe access to food allergy-related services in Canada and the United States (US).
Methods
Participants were recruited via social media from March-July 2021 and were asked to complete an online survey focused on food allergy-related medical care. Participants were Canadian and US residents who live with a child < 18 years old, with ≥ 1 food allergy. A series of logistic regressions were used to assess the associations between country of residence and type of allergy testing utilized during diagnosis.
December 8, 2022
Chronic spontaneous urticaria guidelines: What is new?
Review articles
Urticaria is a heterogeneous inflammatory disorder that can be acute or chronic and is defined by the appearance of wheals, angioedema, or both. Very recently, the newest update and revision of the international European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology/Global Allergy and Asthma European Network/European Dermatology Forum/Asia Pacific Association of Allergy Asthma Clinical Immunology guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria was published. It aims to help primary care physicians and specialists in the management of their patients with urticaria.
December 7, 2022
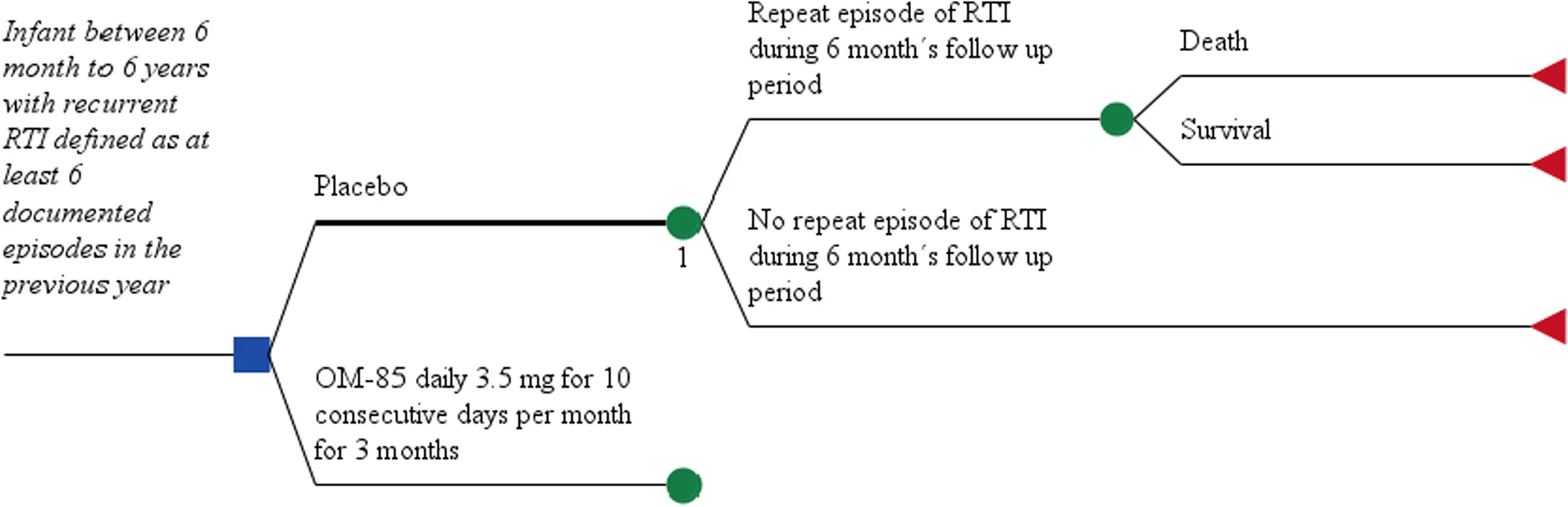
OM-85 BV in pediatric recurrent respiratory tract infections: a cost-utility analysis
- Research Article
- Open Access
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 22, Article number: 465 (2022)
Abstract
Background
Despite the growing evidence on efficacy, little is known regarding the cost-utility of Vaxom/Imocur (OM-85 BV) supplementation to decrease the probability of recurrent respiratory tract infections in OM-85 BV to reduce the incidence of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children.
Methods
A decision tree model was used to estimate the cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) of OM-85 BV in a patient aged 1–6 with a history of recurrent respiratory tract infections.December 5, 2022
Identification by cluster analysis of patients with asthma and nasal symptoms using the MASK-air® mHealth app
Bousquet J, Sousa-Pinto B, Anto JM et al. Pulmonology. 2022 Nov 22:S2531-0437(22)00252-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2022.10.005. Epub ahead of print.
Free article
Abstract
Background: The self-reporting of asthma frequently leads to patient misidentification in epidemiological studies. Strategies combining the triangulation of data sources may help to improve the identification of people with asthma. We aimed to combine information from the self-reporting of asthma, medication use and symptoms to identify asthma patterns in the users of an mHealth app.
Methods: We studied MASK-air® users who reported their daily asthma symptoms (assessed by a 0-100 visual analogue scale - "VAS Asthma") at least three times (either in three different months or in any period). K-means cluster analysis methods were applied to identify asthma patterns based on: (i) whether the user self-reported asthma; (ii) whether the user reported asthma medication use and (iii) VAS asthma.
Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma in Primary Care: Dispensations Do Not Align with Prescriptions
Belhassen M, Bérard M, Devouassoux G, Dalon F, Bousquet J, Van Ganse E. J Asthma Allergy. 2022 Nov 25;15:1721-1729. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S376786.
Free PMC article
Abstract
Background: Appropriate use of effective treatments is required for satisfactory control of allergic symptoms. Coherent medical care -regular prescribing by the same Health Care Professionals- is a preliminary need.
Objective: We investigated the numbers of distinct prescribers, the regularity of medical visits, and the agreement between prescriptions and associated dispensations in individual patients with perennial allergic rhinitis (PAR) and asthma.
Methods: In primary care electronic health records (EHRs), a cohort of patients with PAR and asthma was identified. Individual EHRs were linked to corresponding claims recording all dispensations. Prescribing patterns were analyzed for the major treatment classes, and the dispensations linked to individual prescriptions were retrieved to compute the proportions of days covered (PDCs) for asthma and PAR therapy.
Results: A total of 3654 patients were included, with 62% being female (mean age, 46.1 years). At inclusion, asthma control was not optimal in 51% of the patients and 48% had received oral corticosteroids. The mean interval between successive prescriptions varied between 93 (leukotriene receptor antagonists, LTRAs) and 103 (inhaled corticosteroids, ICS) days, and 97 (antihistamines, AHs) and 103 days (nasal corticosteroids, NCS). On average, individual prescriptions lead to 1.2, 1.5, 1.7 and 1.8 dispensations of ICS, ICS/Long-Acting Beta-Agonist (LABA) fixed-dose combinations, LABAs, and LTRAs, respectively, and to 1.3 and 1.6 dispensations of NCS and AHs, respectively. PDCs then varied between 37.8% for ICS and 58.6% for LTRAs, and between 39.7% for NCS and 50.4% for AHs.
December 4, 2022
Allergen immunotherapy for food allergy: Evidence and outlook
Allergologie select, Volume 6 (2022) - 1st Issue (285 - 292)
Abstract
Food allergy represents a significant health issue characterized by a sizeable epidemiological burden, involving up to 5% of adults and up to 8% of children in the Western world. The elimination diet of the trigger food is the cornerstone of food allergy management. However, novel treatment options are most wanted to provide alternative strategies for this potentially fatal medical condition.
LncRNAs ENST00000499459 and TCONS_00004989 enhance asthma progression in children with house dust mite-induced allergic asthma
- Research
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 18, Article number: 101 (2022)
Abstract
Background
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been extensively reported to play critical roles in the pathogenesis of various disease, especially in cancer. However, little is known about the role of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of pediatric allergic asthma.
Methods
High-throughput sequencing analysis was performed to identify differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 3 children with allergic asthma and 3 matched healthy controls.
December 3, 2022
Interventions for the long term prevention of hereditary angioedema attacks
Abstract
Background
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a serious and potentially life‐threatening condition that causes acute attacks of swelling, pain and reduced quality of life. People with Type I HAE (approximately 80% of all HAE cases) have insufficient amounts of C1 esterase inhibitor (C1‐INH) protein; people with Type II HAE (approximately 20% of all cases) may have normal C1‐INH concentrations, but, due to genetic mutations, these do not function properly. A few people, predominantly females, experience HAE despite having normal C1‐INH levels and C1‐INH function (rare Type III HAE). Several new drugs have been developed to treat acute attacks and prevent recurrence of attacks. There is currently no systematic review and meta‐analysis that included all preventive medications for HAE.
Improving antimicrobial stewardship with penicillin allergy testing: a review of current practices and unmet needs
Abstract
Penicillin allergy, the most frequently reported drug allergy, has been associated with suboptimal antibiotic therapy, increased antimicrobial resistance, increased rates of Clostridioides difficile colonization and infection, as well as extended hospital length of stay and increased cost. Although up to 10% of all patients may report penicillin allergy, most penicillin allergies are not confirmed. As such, most patients with a penicillin allergy can still safely use penicillin and related drugs following a more precise assessment. Herein, we review the current practices and unmet needs in penicillin allergy testing.
December 1, 2022
Monitoring of molecular profiling of allergen-antibody responses in HDM-immunotherapy patients
Marita Nittner-Marszalska 1, Agnieszka Kopeć 1, Aleksandra Foks-Ciekalska 2, Aleksandra Lata 1, Agnieszka Bogacz-Piaseczyńska 2, Marta Rosiek-Biegus 1, Magdalena Zajac 2, Andrzej Bożek 2
Abstract
Among the potential hazards of HDM immunotherapy (AIT) with HDM allergenic extracts is the possible initiation of de novosensitizations caused by a lack of complementarity between a given HDM vaccine's content and a patient's molecular sensitization profile. To investigate whether immunotherapy with HDM extracts affects changes in the profile of sensitizations to allergens contained in the extract and whether neosensitizations occur. Serum samples from patients with HDM allergies (N=63) who received 1 year of treatment with subcutaneous AIT were tested for allergen-specific IgE (sIgE) reactivity to 7 microarrayed HDM allergen molecules (Der p 1, 2,10,11,23; D far 1 and 2) with ImmunoCAP. The HDM non-AIT patients (N=22) who did not receive immunotherapy constituted the study's control group.