Shereen A. Baioumy, Aya Elgendy, Shereen M. Ibrahim, Sara I. Taha & Shaimaa H. Fouad
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 17, Article number: 86 (2021)
Abstract
Background: Increased intestinal permeability, either due to the exposure to antigens in asthmatic patients or due to a barrier defect, plays a critical role in susceptibility to environmental allergens. House dust mite allergy occurs more commonly than any other type of allergy among Egyptian asthmatic patients.
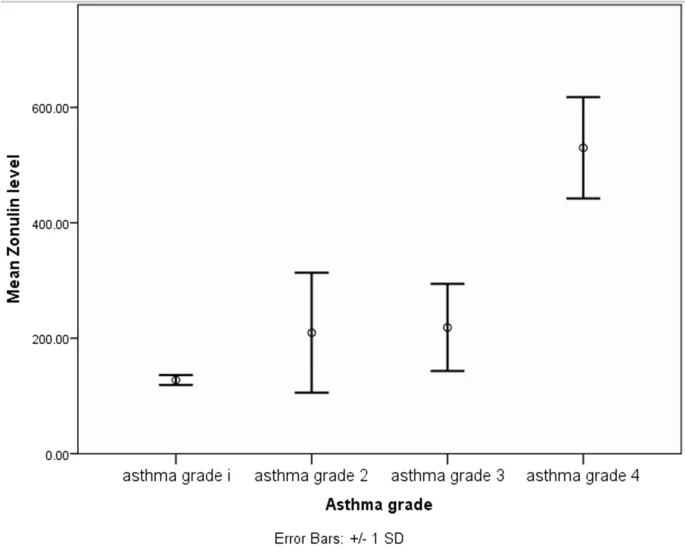
Aim: To assess the relation between serum zonulin level as a marker of increased intestinal permeability and the severity of house dust mite allergic asthma.
Methods: A case–control study which included 48 patients with house dust mite allergic asthma and 48 healthy control subjects attending the Allergy and Immunology Unit, Microbiology and Immunology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University.