Abstract
Respiratory involvement is common in immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD). However, severe asthma as the initial clinical manifestation of IgG4-RD is rare and might be neglected by respiratory clinicians. We aimed to explore the clinical characteristics and prognoses of patients with immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) manifesting as severe asthma.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognoses of patients with severe asthma who were eventually diagnosed with IgG4-RD was performed in the Peking Union Medical College Hospital from 2013 to 2019.
Results
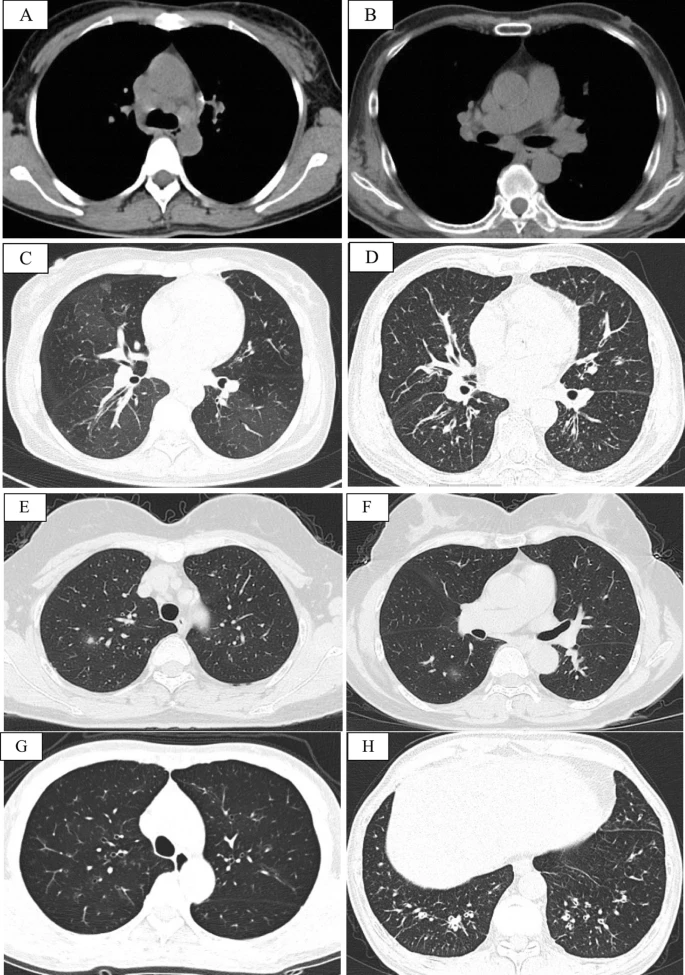
Twelve patients (5males, 7 females) were included. The mean age at enrollment and age of asthma onset were 59.4 ± 10.1 and 53.8 ± 10.4 years, respectively. The mean duration of asthma symptoms was 5.7 ± 2.0 years. In all patients, the proportion (25.1 ± 10.3%) and count (2.0 ± 1.1) × 109/L of eosinophils in peripheral blood increased. Additionally, all patients exhibited elevated total immunoglobulin E [IgE, (1279.3 ± 1257.9) KU/L] and IgG4 (9155.8 ± 9247.6) mg/dL.