Background
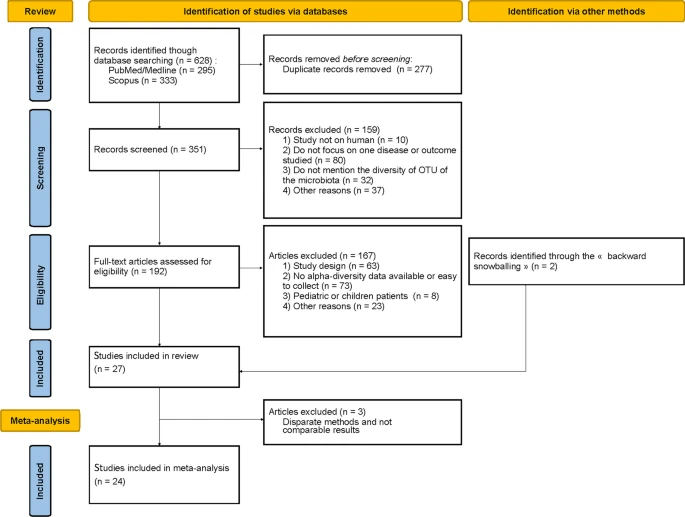 |
| PRISMA flow diagram summarizing our search results and study selection for the systematic review and meta-analysis |
Results
We reviewed 351 articles on title and abstract, of which 27 met our inclusion criteria for systematic review.
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Respiratory Research volume 23, Article number: 214 (2022)
Abstract
 |
| PRISMA flow diagram summarizing our search results and study selection for the systematic review and meta-analysis |
We reviewed 351 articles on title and abstract, of which 27 met our inclusion criteria for systematic review.
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 18, Article number: 75 (2022)
Allergies constitute an important public health problem, and epidemiological data is crucial to developing strategies for its prevention and therapy. Few population-based studies are available for data on allergies and sensitization. However, as these studies are expensive and time-consuming, novel approaches are searched for.
A large monocentric IgE dataset was used to analyse quantitative sensitization data in different age and gender groups and compared the results to available epidemiological data.
A total of 14,370 patients who sought medical care at the Department for Dermatology and Allergology at the Technical University of Munich, Germany was analysed.
Allergic rhinitis and asthma are the most common causes of chronic inflammation of the upper and lower airways in childhood. However, a nasal biomarker that can link to pulmonary inflammation is yet to be found.
Anaphylaxis has increased over the last two decades in Europe, reaching an estimated prevalence of 0.3% and an incidence of 1.5–7.9 per 100,000 person-years. Allergic multimorbidity is associated with asthma severity, yet its role in anaphylaxis is not fully understood. Our aim was to study association between allergic multimorbidity and anaphylaxis in adults.
We used population-based data from the Finnish Allergy Barometer Study (n = 2070, age range: 5–75). Food allergy (FA), atopic dermatitis (AD), allergic rhinitis (AR) and allergic conjunctivitis (AC), were defined from a self-completed questionnaire. A logistic regression adjusted on potential confounders (sex, age, smoking status) was applied to estimate the anaphylaxis risk associated with allergic multimorbidity.
Anaphylaxis was positively associated with the number of allergic diseases a subject exhibited and with subgroups including FA and/or AS. The results can be applied when estimating the risk of anaphylaxis for individual patients.
Wanniang, N., Codreanu-Morel, F., Kuehn, A. et al. Poultry Meat allergy: a Review of Allergens and Clinical Phenotypes. Curr Treat Options Allergy 9, 187–203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-022-00309-2
In the recent years, more cases of poultry meat allergy, both IgE- or non-IgE-mediated, are being reported. Patients have varied clinical reactivity at various levels of sensitivity to different meat preparations. The lack of validated biomarkers renders accurate diagnosis challenging. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of the current status of poultry meat allergy along with a description on the allergens implicated.