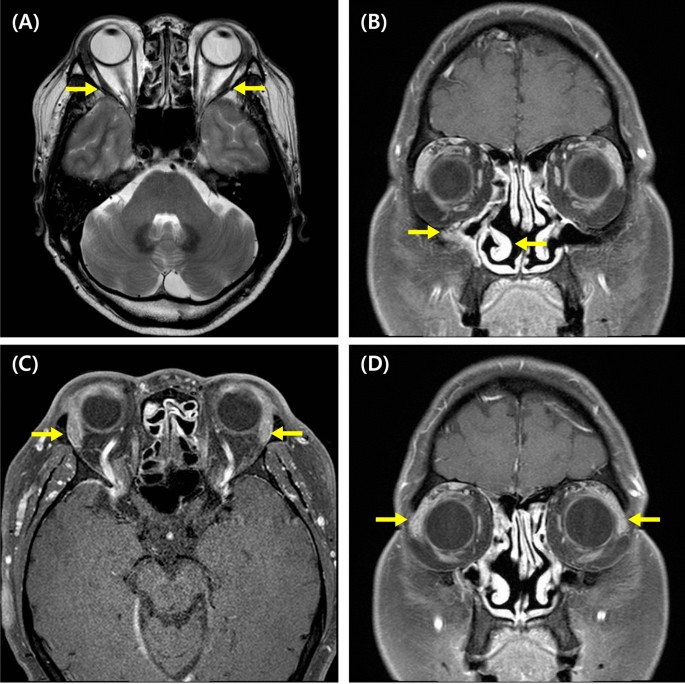
Shaikh N, Hoberman A, Shope TR, et al. JAMA. 2023;330(4):349–358.
Key Points
Question In children aged 2 to 11 years with acute sinusitis, does the efficacy of antibiotic treatment differ based on nasopharyngeal colonization with a bacterial pathogen or by the color of the nasal discharge?
Findings Children without nasopharyngeal bacterial colonization (28% of all enrolled) benefited significantly less from antibiotic treatment than children colonized with pathogens. The effect of antibiotics did not differ based on the color of the nasal discharge.
Meaning In children with acute sinusitis, antibiotic treatment had minimal benefit for those without nasopharyngeal bacterial pathogens. The antibiotic effect did not depend on the color of nasal discharge.
Importance The large overlap between symptoms of acute sinusitis and viral upper respiratory tract infection suggests that certain subgroups of children being diagnosed with acute sinusitis, and subsequently treated with antibiotics, derive little benefit from antibiotic use.