Silver, J., Packnett, E., Park, J. et al. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 19, 104 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-023-00855-7
Abstract
Background
Several biologics are now approved in the US as add-on treatments for chronic rhinosinusitus with nasal polyps (CRSwNP). This cross-sectional, retrospective, real-world study aimed to characterize treatment patterns and identify predictors of biologic use among patients with CRSwNP.
Methods
Adults in the Merative MarketScan Commercial and Medicare Supplemental Databases with medical claims for CRSwNP were identified June 2018–June 2019 (identification period [IP]). Patient characteristics were collated in the IP and treatment pattern data during the IP plus the following year (July 2019–June 2020; observation period [OP]). Data were stratified by sinus surgery and biologic use.
Results
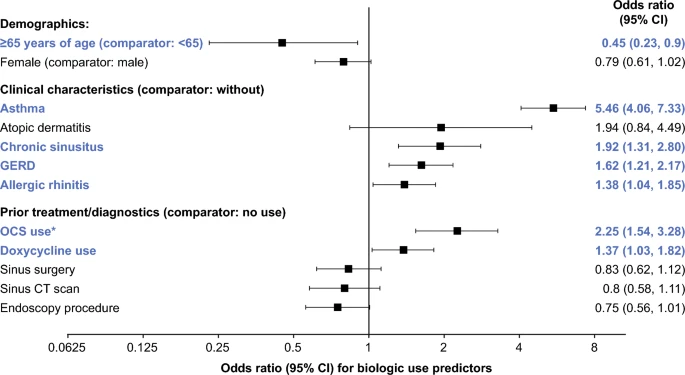
Of the 5997 eligible patients identified (58% male, mean age 48.1 years), 10.7% (n = 642) used biologics during the OP. More biologic users had common respiratory conditions than non-users, particularly asthma (89.1% vs 35.0%; P < 0.001). Biologic users had fewer diagnostic services but more drug-related services than non-users. Only 11.6% of patients who had sinus surgery used biologics, with most (56.1%) having their first biologic dose before sinus surgery and 12.5% ≤ 30 days after. Oral corticosteroid (OCS) use was higher in biologic users than non-users (all patients: 68.8% vs 42.5%; P < 0.001) and in those with/without sinus surgery. Comorbidities, prior OCS/doxycycline use, and age (< 65 years) increased the odds of biologic use, with asthma increasing the odds 5.46 times (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Biologic use was more common before first/next sinus surgery and in patients with high unmet need, elucidating predictors of biologic use that could be used in clinical practice.