Gupte V, Thakur G, Upadhyaya A, et al. (February 27, 2024) Cureus 16(2): e55032. doi:10.7759/cureus.55032Abstract
Introduction: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is increasingly prevalent in India, affecting a significant portion of the population and adversely impacting their quality of life. This nationwide survey aimed to explore the perceptions and clinical preferences of Indian physicians regarding the perceived prevalence, common symptoms, and various available treatments for AR.
Methods: This cross-sectional, observational, digital questionnaire-based survey was conducted from September 2022 to March 2023, involving physicians sharing insights on prevalence rates, diagnostic approaches, medication preferences, and immunotherapy practices in AR management.
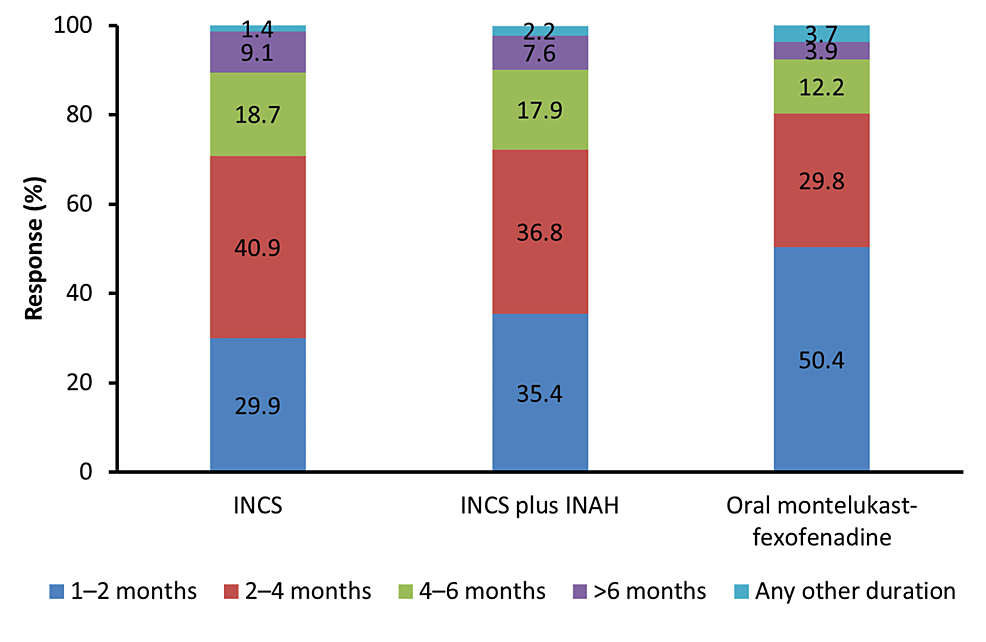 |
| Recommended duration of therapy with different molecules |
Results: A total of 1608 physicians participated in this survey. The majority of physicians (n=684, 42.5%) reported that the prevalence of AR in routine clinical practice is between 21 and 40%. Physicians also noted a substantial burden of AR with asthma (n=626, around 40%). Total IgE count was reported as a mandatory test for the diagnosis of AR by 47.5% of physicians (n=764). For the management of mild cases of seasonal or perennial AR, 980 (60.9%) physicians preferred fexofenadine as an oral antihistamine of choice. Fluticasone furoate was the preferred intranasal corticosteroid (INCS) option (67.1% of physicians (n=1079)), for the management of patients with moderate to severe AR, the most recommended duration of INCS therapy was two to four months (40.9% of physicians).