Abstract
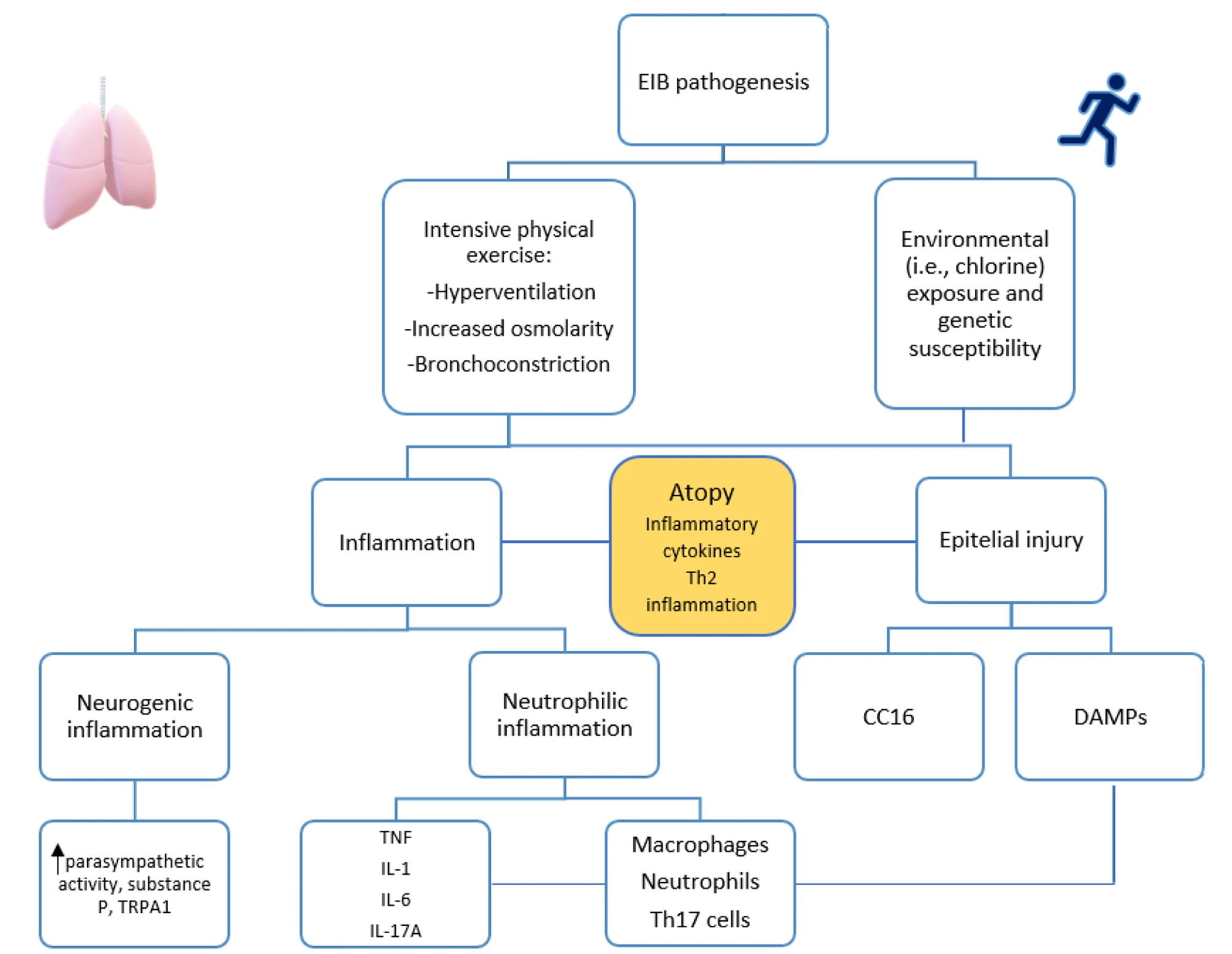 |
| EIB pathogenesis and the central role of atopy |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Abstract
 |
| EIB pathogenesis and the central role of atopy |
Abstract
Background:
Anaphylaxis represents the most severe end of the spectrum of allergic reactions. Frequent elicitors of anaphylaxis are insects, foods, and drugs. This paper summarizes recent development with regard to emerging and novel elicitors of anaphylaxis.
Summary:
 |
| Allergens in selected plant foods with increasing importance in anaphylaxis cases |
Abstract
Purpose: Despite the risk of anaphylaxis, oral food challenges (OFCs) are performed clinically for various indications, particularly to confirm tolerance development. This study aimed to assess OFCs by relevant indications and build an outcome prediction model to help determine when to perform OFCs in children who are likely to have developed immune tolerance.
Methods: In total, 432 pediatric OFCs were retrospectively analyzed according to indications. Clinical characteristics, serum total immunoglobulin (Ig) E, blood eosinophils, and specific IgE and IgG4 levels for food allergens were noted and compared. Machine learning was utilized to select the most important variables in determining the passage of the OFCs, and prediction models were constructed using the selected variables.
Results: OFCs were most commonly performed to confirm tolerance development (number, %; 267, 61.8%). The most common food allergens tested were egg (191, 44.2%) and milk (135, 31.3%). 
Distribution of oral food challenge results based on age
and food-specific immunoglobulin E for egg white and cow’s milk.
Cherrez-Ojeda I, Gallardo-Bastidas JC, Borrero GR et al. BDJ Open. 2024 Apr 4;10(1):28. doi: 10.1038/s41405-024-00210-x.
Abstract
Objective/aim
The absence of a comprehensive understanding of potential anaphylactic reactions to local anesthetics (LAs) and management can result in grave consequences. For this reason we aim to assess Latin American dentists’ knowledge, preparedness, and competency in managing anaphylactic reactions to LAs.
Materials and Methods
Design: A cross-sectional study was conducted from November 2021 to February 2022. Board-certified dentists answered a survey comprising 26 structured questions. Chi-square tests and logistic regression models were performed in Stata 17.0. Setting: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, Peru, Venezuela, and other Latin American countries.
Abstract
Background
Managing a pregnant patient with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is often challenging. Recent data have shown that most CSU treatments in pregnant patients are second-generation H1 antihistamines (sgAHs), while data on the safety of omalizumab are scant.
Objectives
To evaluate, in a routine clinical practice setting, the efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with severe CSU refractory to sgAHs who either became pregnant during treatment or who started the drug during pregnancy.
Abstract
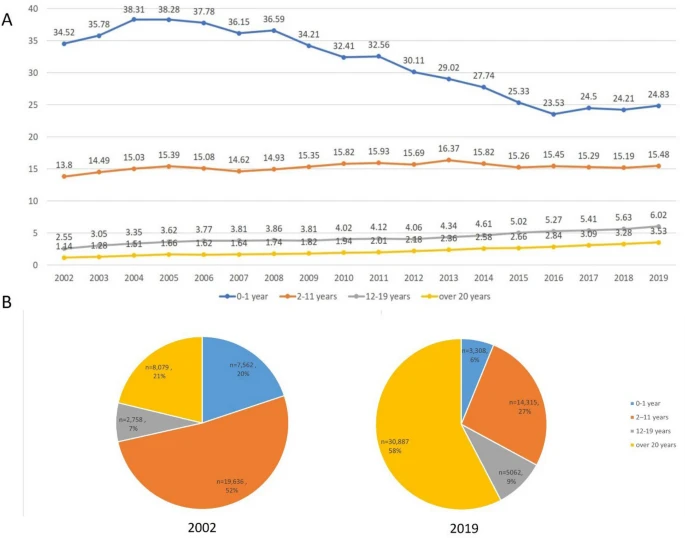 |
| A) Change of annual prevalence of atopic dermatitis according to age group from 2002 to 2019, (B) distribution of atopic dermatitis patients by age group in 2002 and in 2019. |
 |
| Graphical Abstract |