Li Y, Peng R, Xue J, Zhao Y. Acta Derm Venereol. 2025 Aug 3;105:adv43568. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v105.43568.
Abstract
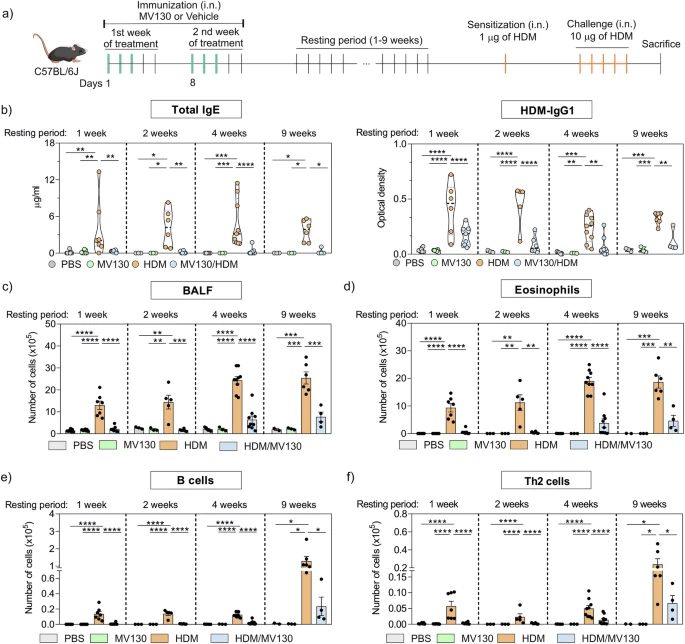
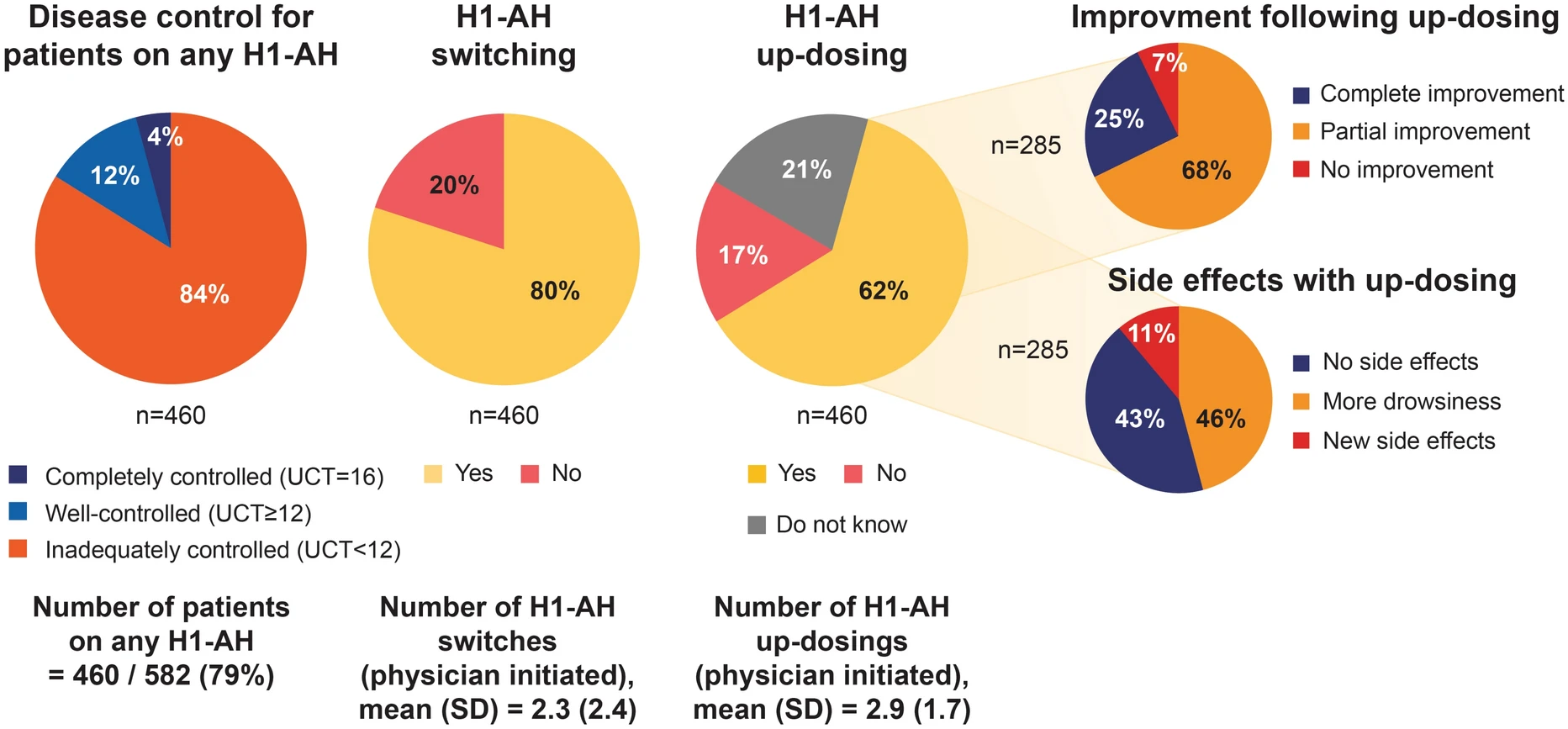
Chronic spontaneous urticaria is a common skin disorder with variable treatment responses. Second-generation H1-antihistamines are the first-line treatment for chronic spontaneous urticaria, yet many patients fail to respond to licensed doses. Predictors of treatment response to second-generation H1-antihistamines could help optimize disease management and minimize unnecessary healthcare costs. In this retrospective cohort study of 99 Chinese chronic spontaneous urticaria patients, higher log-transformed serum total IgE levels were significantly associated with poor response to standard-dose antihistamines (aOR = 2.09, 95% CI: 1.29–3.38, p = 0.003).