P. E. Vonk, J. J. Otten, H. B. E. Elzinga, et al. Allergy (2025): 1–10, https://doi.org/10.1111/all.70151.
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
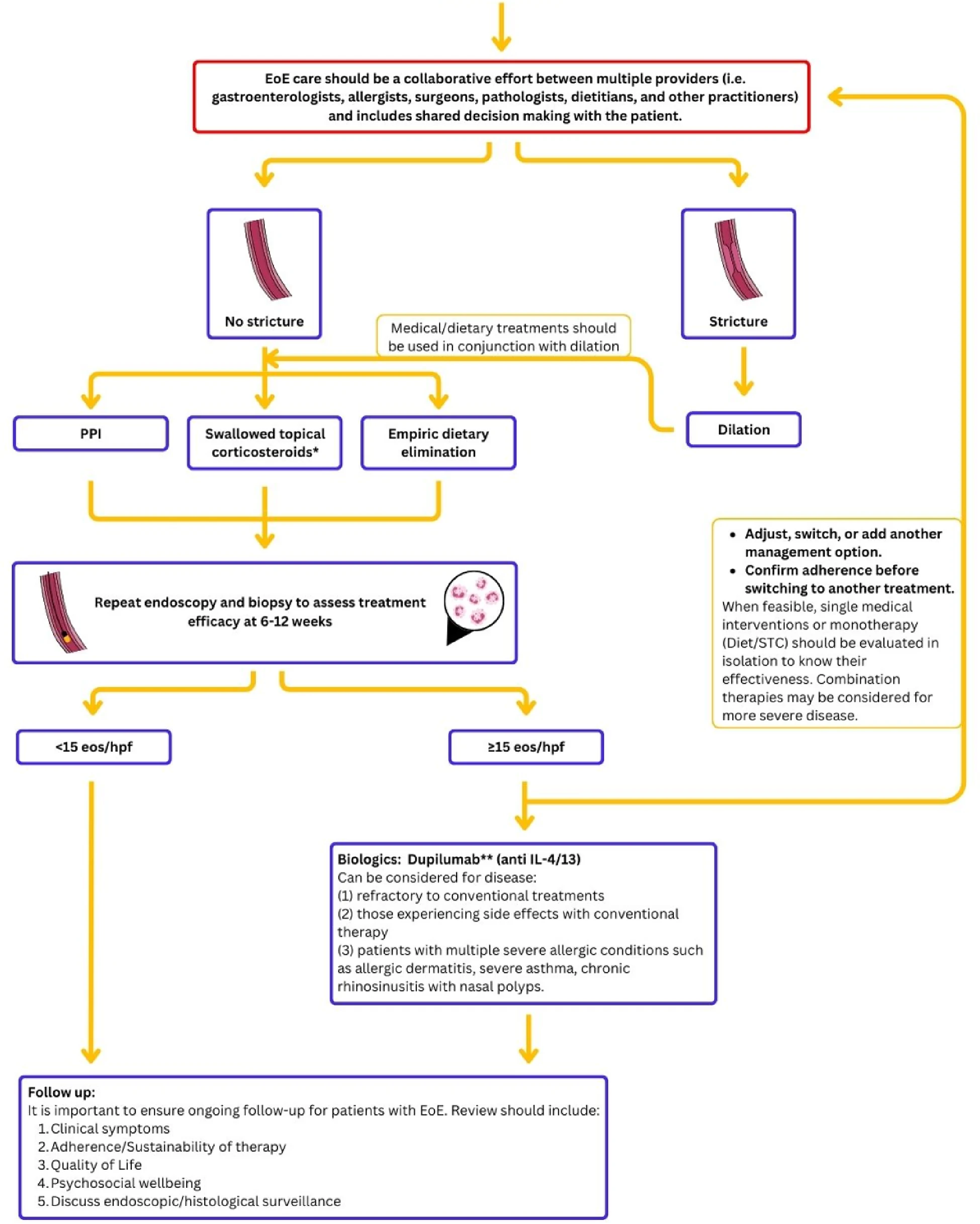
Background
Dupilumab is effective in treating patients with type-2 dominant chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (T2-CRSwNP). Dosing starts at an interval of 1×/2 weeks (Q2W) with possible tapering upon disease control. Prolonging the interdose interval reduces patient burden and side effects and improves cost-effectiveness.
Objectives
(1) Analyze how many patients successfully reach and maintain extended tapering of at least 1×/12 weeks (Q12W), (2) evaluate differences in baseline characteristics and clinical measurements between patients who maintain disease control on ≥ Q12W (“super-responders”) and patients who do not; (3) compare characteristics of “super-responders” to patients reaching Q12W but losing disease control on that dose (“excellent responders”).