Xiang, YK., Türk, M., Ojeda, I.C. et al. Curr Treat Options Allergy 11, 194–210 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-024-00375-8
Abstract
Purpose of review
The goal of this review is to examine the relationship between psychological stress and chronic urticaria (CU), focusing on the underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions. The paper seeks to answer how stress exacerbates CU and the neuro-immunological pathways involved, providing insight into improving therapeutic strategies by considering the psychological dimensions of the disease.
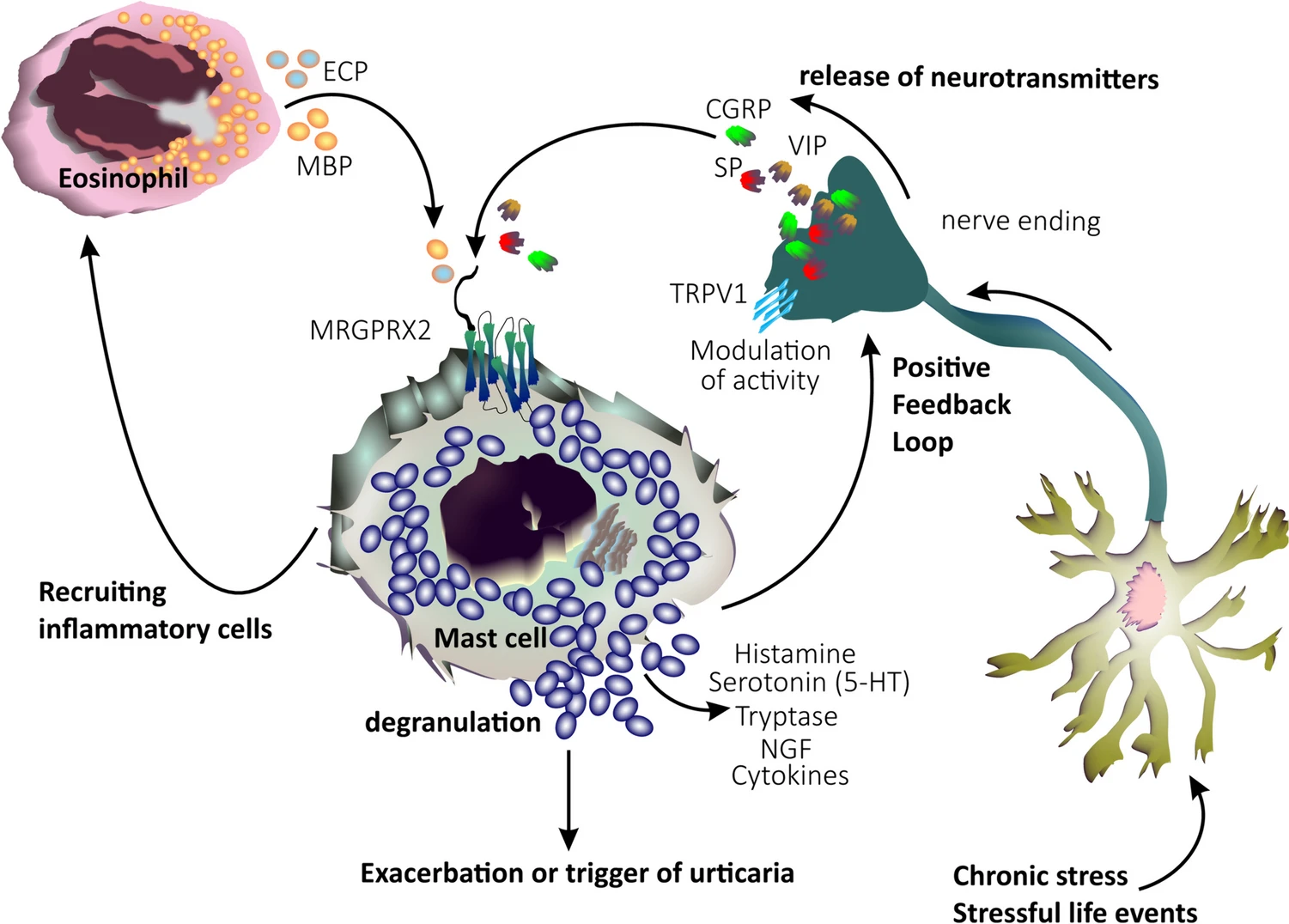 |
Recent studies highlight the significant role of stress in aggravating CU through the dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and neurogenic inflammation. Increased levels of neuropeptides like substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide, as well as upregulated expression of the MRGPRX2 receptor, are implicated in the neuro-immune interactions that worsen CU symptoms.