Abstract
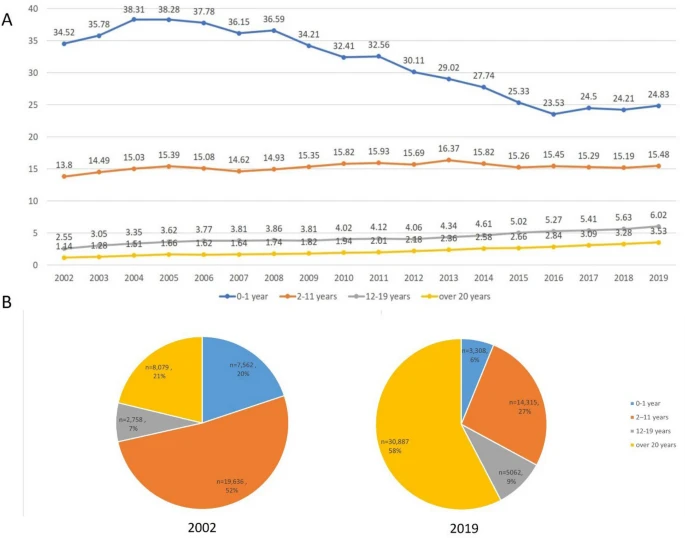 |
| A) Change of annual prevalence of atopic dermatitis according to age group from 2002 to 2019, (B) distribution of atopic dermatitis patients by age group in 2002 and in 2019. |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Abstract
 |
| A) Change of annual prevalence of atopic dermatitis according to age group from 2002 to 2019, (B) distribution of atopic dermatitis patients by age group in 2002 and in 2019. |
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
Key Points
Question Is there an association between human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX)/cotrimoxazole (CTX)–induced severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs)?
Findings In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 6 studies involving 322 patients with SCARs, significant associations were identified between the HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*13:01, HLA-B*15:02, HLA-B*38:02, and HLA-C*08:01 genotypes and SMX/CTX-induced SCARs. The HLA-B*15:02 and HLA-B*38:02 genotypes were significantly associated with SMX/CTX-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), while the HLA-A*68:01 and HLA-B*39:01 genotypes were associated with SMX/CTX-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; the HLA-B*13:01 allele showed an association with SMX/CTX-induced SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.
Meaning The results of this review suggest that multiple HLA alleles were associated with SMX/CTX-induced SCARs.
Abstract
Importance Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and cotrimoxazole (CTX), a fixed-dose combination of SMX and trimethoprim in a 5:1 ratio, are antibacterial sulfonamides commonly used for treating various diseases.
Li Y, Xiao H, Zeng Y, Tang Y, Zhou L, Liu W. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Feb 11;23(1):52-58. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v23i1.14953.
AbstractAllergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) has confirmed its efficacy in improving the symptoms of allergic rhinitis. However, no reliable biomarkers have been identified to predict the efficacy of AIT were found. We aimed to find clinical and immunological markers to predict efficacy in children after 2 years of sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). A total of 285 children diagnosed with allergic rhinitis were recruited.
The clinical efficacy was evaluated by comparing endpoint and baseline symptom and medication scores (SMS). Baseline clinical and immunological markers (serum total and specific immunoglobulin [Ig]E) and their correlation with clinical efficacy were analyzed.
Abstract
Objective
This study aims to assess the outcome of challenging documented moderate, severe, or unknown beta-lactam allergies with full dose administration of a beta-lactam antibiotic in emergency department (ED) patients admitted for acute bacterial infection.
Methods
A single-center, retrospective, descriptive study of adult patients challenged with a full dose of beta-lactam in the ED from January 2021 to December 2022 was conducted. Included patients had at least one documented moderate, severe, or unknown beta-lactam allergy in the electronic medical record (EMR) without documentation of prior tolerance. Patient demographics, prior beta-lactam antibiotic reaction, beta-lactam administered in the ED, inpatient beta-lactam continuation, adverse drug reactions, and updates to allergy profiles were collected. Descriptive statistics for data analysis were performed using SPSS Version 22.Bangert, C., Alkon, N., Chennareddy, S. et al. Nat Commun 15, 2839 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46540-0
Abstract
Dupilumab, an IL4R-blocking antibody, has shown clinical efficacy for atopic dermatitis (AD) treatment. In addition to conjunctivitis/blepharitis, the de novo appearance of head/neck dermatitis is now recognized as a distinct side effect, occurring in up to 10% of patients. Histopathological features distinct from AD suggest a drug effect, but exact underlying mechanisms remain unknown. We profiled punch biopsies from dupilumab-associated head and neck dermatitis (DAHND) by using single-cell RNA sequencing and compared data with untreated AD and healthy control skin.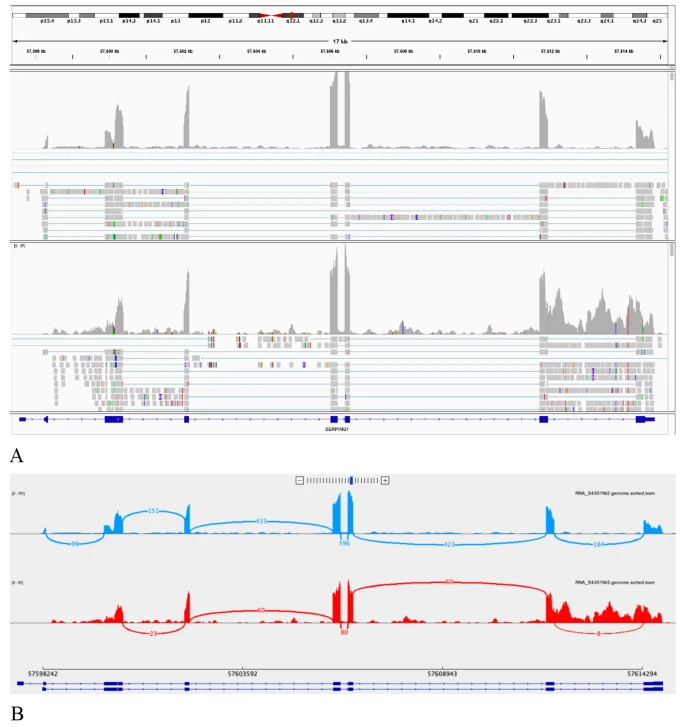 |
| Retention of the last SERPING1 intron present due to the NM_000062.2:c.1249 + 4 A > G r.spl variant found in patient no. 9 using transcriptome sequencing. |