Kim H, Jeong K, Park M et al. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Mar;16(2):179-190. doi: 10.4168/aair.2024.16.2.179.Abstract
Purpose: Despite the risk of anaphylaxis, oral food challenges (OFCs) are performed clinically for various indications, particularly to confirm tolerance development. This study aimed to assess OFCs by relevant indications and build an outcome prediction model to help determine when to perform OFCs in children who are likely to have developed immune tolerance.
Methods: In total, 432 pediatric OFCs were retrospectively analyzed according to indications. Clinical characteristics, serum total immunoglobulin (Ig) E, blood eosinophils, and specific IgE and IgG4 levels for food allergens were noted and compared. Machine learning was utilized to select the most important variables in determining the passage of the OFCs, and prediction models were constructed using the selected variables.
 |
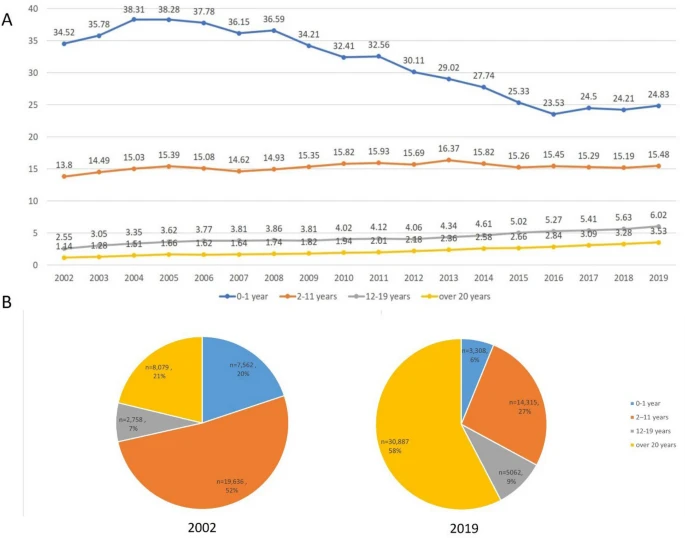
Distribution of oral food challenge results based on age
and food-specific immunoglobulin E for egg white and cow’s milk. |
Results: OFCs were most commonly performed to confirm tolerance development (number, %; 267, 61.8%). The most common food allergens tested were egg (191, 44.2%) and milk (135, 31.3%).