- Letter to the Editor
- Open Access
Abstract
Background
In daily practice, one-third of sesame allergic patients, confirmed by clinical history or food challenge, do not show any detectable specific IgE using current diagnostics. Currently used sesame extracts are water-based and therefore lacking hydrophobic proteins like oleosins.
Oleosins, the stabilizer of lipid droplets in plants, are described as allergens in sesame, peanut and hazelnut. In this study, we examine the role of oleosins in sesame allergy and their potential cross-reactivity between sesame and (pea)nuts.
Methods
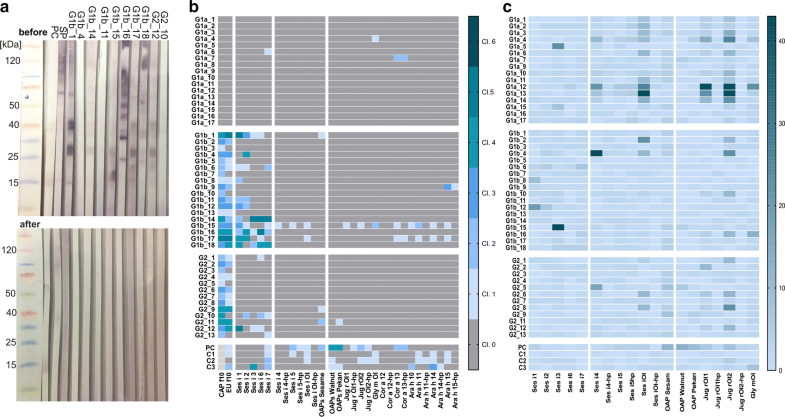
Specific IgE and IgG sensitisation to native and heterologously expressed sesame components and oleosins from other nuts, free of seed storage proteins, was assessed by line blot and sera from 17 sesame allergic patients without detectable specific IgE sensitisation to sesame, and compared to 18 sesame allergic and 13 tolerant patients with specific IgE sensitisation to sesame.
Results
Sesame allergic patients without sensitisation showed no specific IgE to the tested sesame oleosins or components. Low levels of specific IgE to sesame oleosins were detected in 17% of sesame allergic and 15% of tolerant patients with sIgE sensitisation. Oleosins were recognised by serum IgG from multiple patients confirming immune reactivity and excluding technical issues leading to lack of specific IgE-binding to oleosins.
Conclusion
Sesame oleosins are minor allergens and appear to have no additonal value in diagnosing sesame allergy in adults based on sIgE and sIgG detection. There is a high need for additional diagnostic tools in those patients to minimize the number of required food challenges.
No comments:
Post a Comment