- Technical advance
- OPEN Open Peer Review
BMC Pulmonary Medicine
Mattis Gottlow,
David J. Svensson,
Ilya Lipkovich,
Monika Huhn,
Karin Bowen,
Peter Wessman &
Gene Colice
BMC Pulmonary Medicine
BMC Pulmonary Medicine 19, Article number: 129 (2019)
Abstract
Background
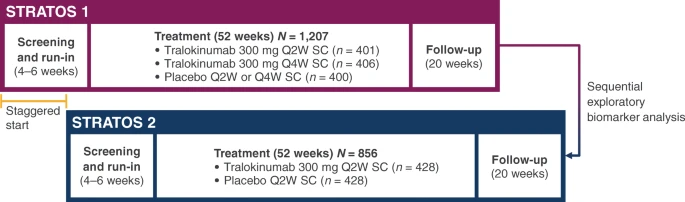 |
| Staggered trial design of STRATOS 1 and 2. Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks; SC, subcutaneous |
Tralokinumab is an anti–interleukin (IL)-13 monoclonal antibody investigated for the treatment of severe, uncontrolled asthma in two Phase III clinical trials, STRATOS 1 and 2. The STRATOS 1 biomarker analysis plan was developed to identify biomarker(s) indicative of IL-13 activation likely to predict tralokinumab efficacy and define a population in which there was an enhanced treatment effect; this defined population was then tested in STRATOS 2.
Methods
The biomarkers considered were blood eosinophil counts, fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), serum dipeptidyl peptidase-4, serum periostin and total serum immunoglobulin E. Tralokinumab efficacy was measured as the reduction in annualised asthma exacerbation rate (AAER) compared with placebo (primary endpoint measure of STRATOS 1 and 2). The biomarker analysis plan included negative binomial and generalised additive models, and the Subgroup Identification based on Differential Effect Search (SIDES) algorithm, supported by robustness and sensitivity checks. Effects on the key secondary endpoints of STRATOS 1 and 2, which included changes from baseline in standard measures of asthma outcomes, were also investigated. Prior to the STRATOS 1 read-out, numerous simulations of the methodology were performed with hypothetical data.
Results
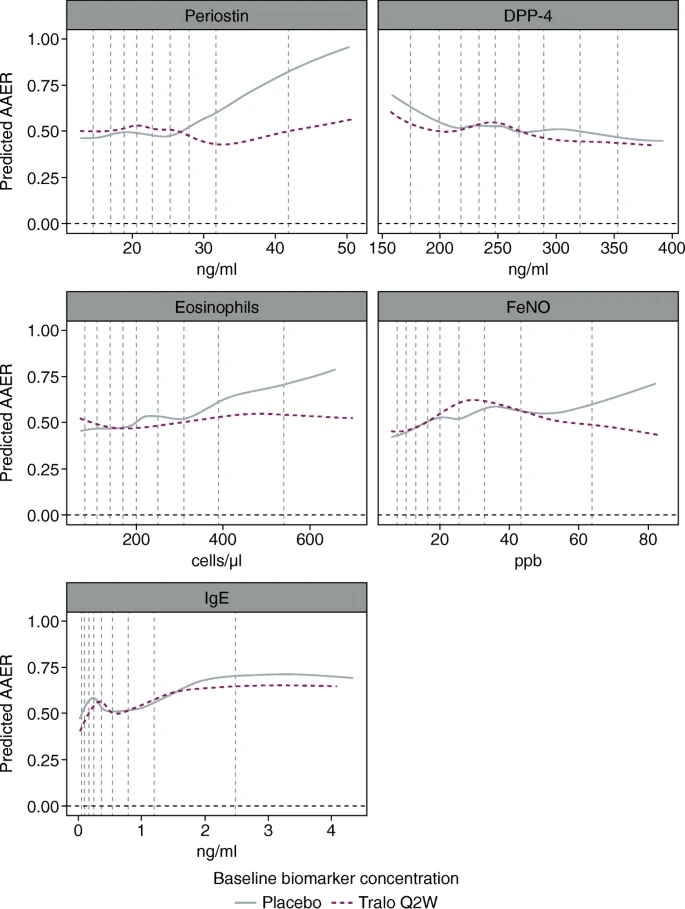
FeNO and periostin were identified as the only biomarkers potentially predictive of treatment effect, with cut-offs chosen by the SIDES algorithm of > 32.3 ppb and > 27.4 ng/ml, respectively. The FeNO > 32.3 ppb subgroup was associated with greater AAER reductions and improvements in key secondary endpoints compared with the periostin > 27.4 ng/ml subgroup. Upon further evaluation of AAER reductions at different FeNO cut-offs, ≥37 ppb was chosen as the best cut-off for predicting tralokinumab efficacy.
Discussion
A rigorous statistical approach incorporating multiple methods was used to investigate the predictive properties of five potential biomarkers and to identify a participant subgroup that demonstrated an enhanced tralokinumab treatment effect. Using STRATOS 1 data, our analyses identified FeNO at a cut-off of ≥37 ppb as the best assessed biomarker for predicting enhanced treatment effect to be tested in STRATOS 2. Our findings were inconclusive, which reflects the complexity of subgroup identification in the severe asthma population.
No comments:
Post a Comment