- Letter to the Editor
- Open Access Clinical and Translational Allergy
Clinical and Translational Allergy20199:35
Abstract
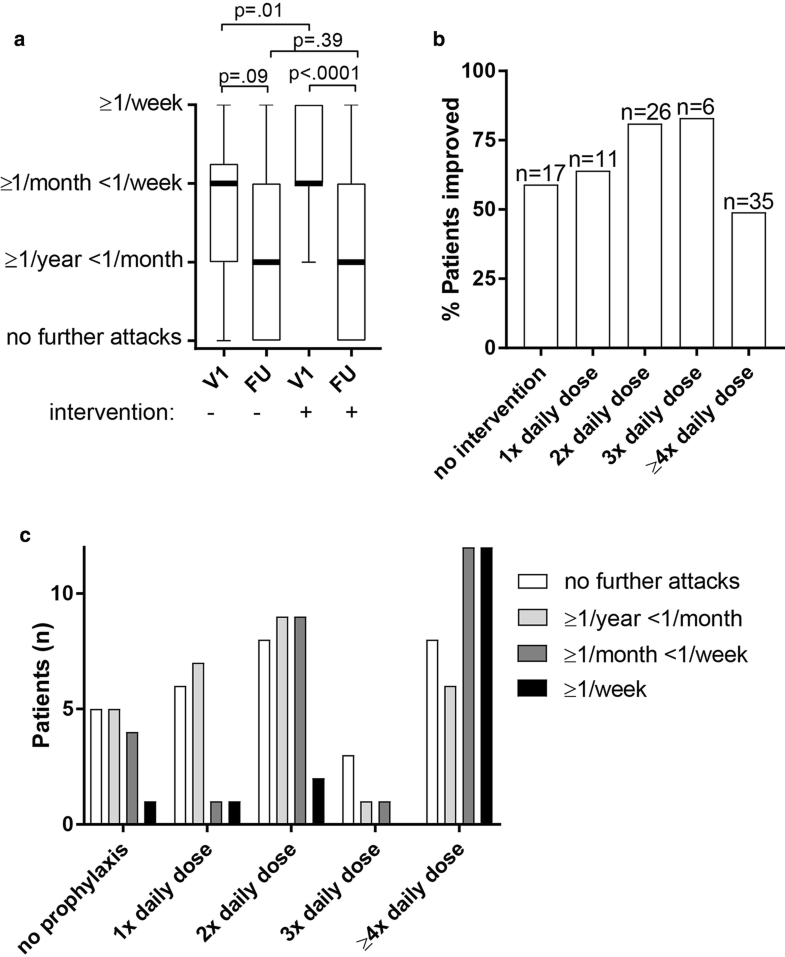
Antihistamines are the most prescribed therapy in recurrent idiopathic angioedema, yet little is known about their efficacy. Herein, we report on clinical improvement with antihistamine therapy in 120 patients evaluating angioedema attack frequency. A high incidence (36%) of antihistamine refractory cases was observed.
No comments:
Post a Comment