- Research article
- Open Access
- Open Peer Review
Abstract
Background
Several major randomized control studies have demonstrated that mepolizumab, an anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody, is effective for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma who show exacerbation or require systemic corticosteroid maintenance therapy. However, the predictive factors of the response to mepolizumab other than blood eosinophil count are unclear in clinical practice.
Objective
To elucidate the predictive factors of the response to mepolizumab for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma.
Methods
From July 2016 to December 2017, 28 patients with severe asthma received mepolizumab in our hospital. To determine the predictive factors, we retrospectively evaluated patient characteristics, comorbidities, biomarkers, pulmonary function, maintenance dose of systemic corticosteroids and number of exacerbations.
Results
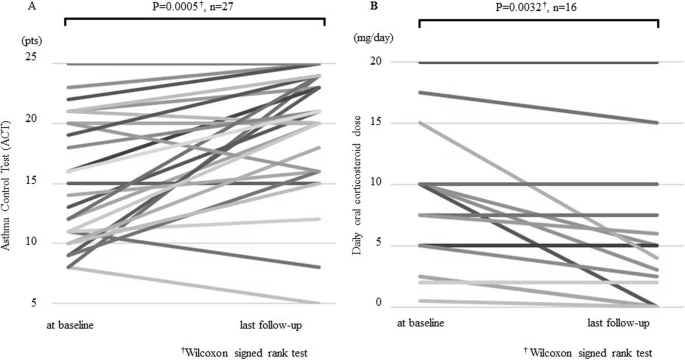
The response rate to mepolizumab treatment was 70% (19/27; one pregnant woman was excluded from analysis). Compared with 11 patients without eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS), 16 patients with ECRS showed significantly improved systemic corticosteroid-sparing effects [− 71.3 ± 37.0% vs − 10.7 ± 20.1%, P = 0.006], change from baseline FeNO [− 19 ± 57 (%) vs 30 ± 77 (%), P = 0.023] and symptoms [14 patients (88%) vs five patients (45%), P = 0.033]. ECRS was identified as a predictive factor of the response to mepolizumab in a multivariate logistic regression analysis [odds ratio = 22.5, 95% CI (1.5–336), P = 0.024]. Of the eight patients previously administered omalizumab, five responded to mepolizumab. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B IgE results were negative in 80% of responders (P = 0.14).
Conclusion
Both groups showed improved symptom scores and a decreased number of exacerbations. Mepolizumab substantially improved the clinical variables of patients with eosinophilic asthma complicated with ECRS.
No comments:
Post a Comment