Respiratory Research Research- Open Access
Dehan Liu, Wanshu Zhang, Feng Pan, Lin Li, Lian Yang, Dandan Zheng, Jiazheng Wang & Bo Liang Respiratory Research volume 21, Article number: 125 (2020)
Dehan Liu, Wanshu Zhang, Feng Pan, Lin Li, Lian Yang, Dandan Zheng, Jiazheng Wang & Bo Liang Respiratory Research volume 21, Article number: 125 (2020)
Abstract
Background
A cluster of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia were discharged from hospitals in Wuhan, China. We aimed to determine the cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution at each time point, to explore the relevant affecting factors, and to describe the chest CT findings at different time points after hospital discharge.
Methods
Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia confirmed by RT-PCR who were discharged consecutively from the hospital between 5 February 2020 and 10 March 2020 and who underwent serial chest CT scans on schedule were enrolled. The radiological characteristics of all patients were collected and analysed. The total CT score was the sum of non-GGO involvement determined at discharge. Afterwards, all patients underwent chest CT scans during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd weeks after discharge. Imaging features and distributions were analysed across different time points.
Results
Background
A cluster of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia were discharged from hospitals in Wuhan, China. We aimed to determine the cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution at each time point, to explore the relevant affecting factors, and to describe the chest CT findings at different time points after hospital discharge.
Methods
Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia confirmed by RT-PCR who were discharged consecutively from the hospital between 5 February 2020 and 10 March 2020 and who underwent serial chest CT scans on schedule were enrolled. The radiological characteristics of all patients were collected and analysed. The total CT score was the sum of non-GGO involvement determined at discharge. Afterwards, all patients underwent chest CT scans during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd weeks after discharge. Imaging features and distributions were analysed across different time points.
Results
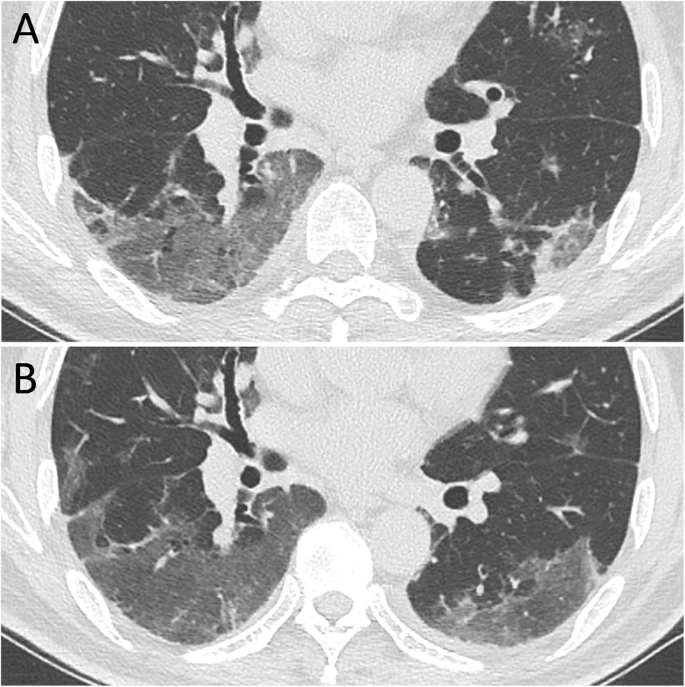
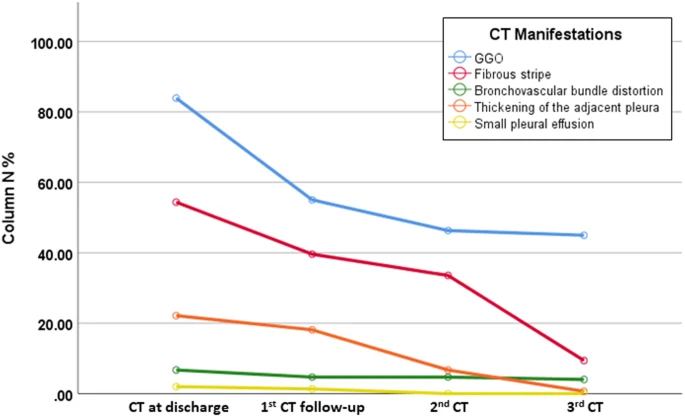 A total of 149 patients who completed all CT scans were evaluated; there were 67 (45.0%) men and 82 (55.0%) women, with a median age of 43 years old (IQR 36–56). The cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution was 8.1% (12 patients), 41.6% (62), 50.3% (75), and 53.0% (79) at discharge and during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd weeks after discharge, respectively. Patients ≤44 years old showed a significantly higher cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution than patients > 44 years old at the 3-week follow-up. The predominant patterns of abnormalities observed at discharge were ground-glass opacity (GGO) (125 [83.9%]), fibrous stripe (81 [54.4%]), and thickening of the adjacent pleura (33 [22.1%]). The positive count of GGO, fibrous stripe and thickening of the adjacent pleura gradually decreased, while GGO and fibrous stripe showed obvious resolution during the first week and the third week after discharge, respectively. “Tinted” sign and bronchovascular bundle distortion as two special features were discovered during the evolution.
A total of 149 patients who completed all CT scans were evaluated; there were 67 (45.0%) men and 82 (55.0%) women, with a median age of 43 years old (IQR 36–56). The cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution was 8.1% (12 patients), 41.6% (62), 50.3% (75), and 53.0% (79) at discharge and during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd weeks after discharge, respectively. Patients ≤44 years old showed a significantly higher cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution than patients > 44 years old at the 3-week follow-up. The predominant patterns of abnormalities observed at discharge were ground-glass opacity (GGO) (125 [83.9%]), fibrous stripe (81 [54.4%]), and thickening of the adjacent pleura (33 [22.1%]). The positive count of GGO, fibrous stripe and thickening of the adjacent pleura gradually decreased, while GGO and fibrous stripe showed obvious resolution during the first week and the third week after discharge, respectively. “Tinted” sign and bronchovascular bundle distortion as two special features were discovered during the evolution.Conclusion
Lung lesions in COVID-19 pneumonia patients can be absorbed completely during short-term follow-up with no sequelae. Two weeks after discharge might be the optimal time point for early radiological estimation.
No comments:
Post a Comment