- Research
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 17, Article number: 41 (2021)
The epidemiologic impact of hereditary angioedema (HAE) is difficult to quantify, due to misclassification in retrospective studies resulting from non-specific diagnostic coding. The aim of this study was to identify cohorts of patients with HAE-1/2 by evaluating structured and unstructured data in a US ambulatory electronic medical record (EMR) database.
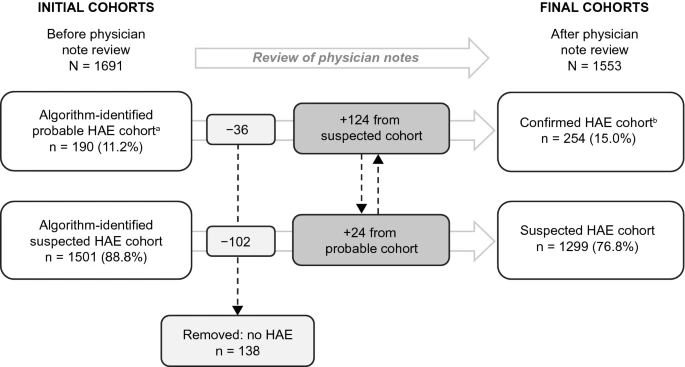
A retrospective feasibility study was performed using the GE Centricity EMR Database (2006–2017). Patients with ≥ 1 diagnosis code for HAE-1/2 (International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification 277.6 or International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification D84.1) and/or ≥ 1 physician note regarding HAE-1/2 and ≥ 6 months’ data before and after the earliest code or note (index date) were included. Two mutually exclusive cohorts were created: probable HAE (≥ 2 codes or ≥ 2 notes on separate days) and suspected HAE (only 1 code or note). The impact of manually reviewing physician notes on cohort formation was assessed, and demographic and clinical characteristics of the 2 final cohorts were described.
Unstructured EMR data can provide valuable information for identifying patients with HAE-1/2. Further research is needed to develop algorithms for more representative HAE cohorts in retrospective studies.
No comments:
Post a Comment