- Research
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 17, Article number: 74 (2021)
CD8+CD25+fork-head box transcription factor (Foxp3)+ regulatory T cells (CD8+ Tregs) play a role in immune tolerance. However, the role of these cells in allergic rhinitis (AR) has not been elucidated. The study aimed to evaluate influences of CD8+ Tregs on inflammatory conditions in a murine model of AR.
A murine model of AR was established. CD8+ Tregs were isolated from mice nasal mucosa and cultured in vitro. We examined interleukin (IL)-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β in cell cultures. Then, we administered CD8+ Tregs into mice nasal mucosal cultures, and examined eosinophil cation protein (ECP), IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 in these cultures. Finally, we adoptively transferred CD8+ Tregs into mice models, and evaluated percentages of CD8+ Tregs, numbers of sneezing and nasal rubbing, and counts of eosinophils and contents of ECP, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-10 and TGF-β in nasal lavage fluid (NLF) in mice.
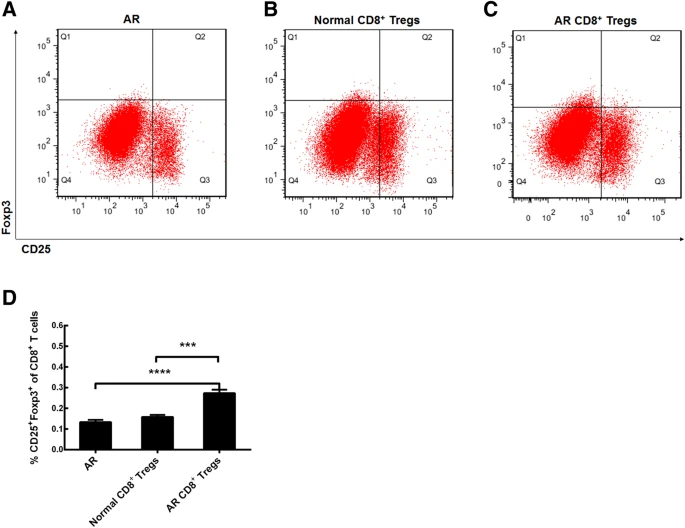
The percentage of CD8+ Tregs from AR mice was reduced. IL-10 and TGF-β were increased in cell cultures from AR mice. ECP, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 were decreased after the AR mice CD8+ Tregs administration in mucosal cultures. However, their contents were not changed after normal CD8+ Tregs treatment. Additionally, the adoptive transfer of AR CD8+ Tregs enhanced the percentage of CD8+ Tregs and levels of IL-10 and TGF-β in NLF, reduced numbers of sneezing and nasal rubbing, and counts of eosinophils and concentrations of ECP, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 in NLF. However, normal CD8+ Tregs could not change above parameters.
These findings show that CD8+ Tregs may inhibit inflammatory responses in the AR condition.
No comments:
Post a Comment