- Research
- Open Access
Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease (IgG4-RLD) is a rare entity. We retrospectively analyzed the clinical and histopathological characteristics of patients with pathologically confirmed IgG4-RLD to improve the diagnosis rate and reduce the risk of misdiagnosis.
We screened the pathological reports of 4838 patients with pulmonary surgery and/or biopsy specimens from April 2017 to April 2021 at Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital affiliated with Sun Yat-Sen University, and specimens from 65 patients with suspected IgG4-RLD were subjected to immunohistochemical staining for IgG4 and IgG. Finally, 10 patients with definite IgG4-RLD that was pathologically confirmed were enrolled and analyzed.
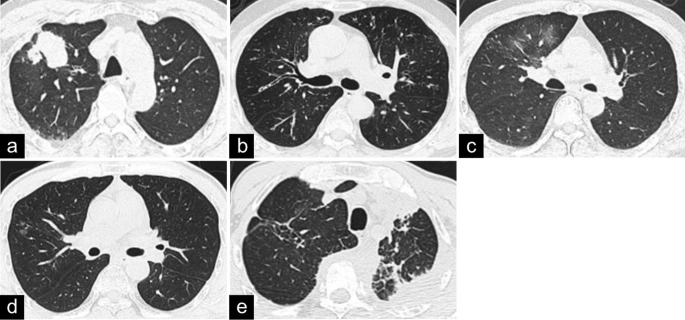
The incidence of pathologically confirmed IgG4-RLD was 0.2% (10/4838). The ten patients had an average age of 59.7 years at diagnosis, and the male-to-female ratio was 9:1. The initial clinical manifestations were nonspecific, and cough was the most common symptom (4/10). More than one organ was involved in most patients (8/10), and mediastinal/hilar lymph node involvement was often observed (7/10). Serum IgG4 was analyzed in 6 patients and found to be elevated. Serum tumor marker levels were within the normal range or were slightly elevated. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest and/or 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (18F-FDG PET-CT) imaging revealed that 5 patients had a mixed type, 3 patients had the solid nodular type, and 2 patients had the bronchovascular type. All pulmonary masses and large nodules with solid patterns had spiculated margins and inhomogeneous enhancement with or without pleural indentation and a lobulated appearance. Abundant lymphoplasmacytic cell infiltration and fibrosis were observed in all patients. The expression of IgG4 and IgG was upregulated in the pulmonary sections. Seven patients were treated with glucocorticoids with or without additional immunosuppressants and responded well.
The results of our study suggest that multiple imaging findings, an elevated serum IgG4 concentration, and no significant increase in serum tumor biomarkers could provide diagnostic support for IgG4-RLD, especially for isolated IgG4-RLD or IgG4-RLD that includes other organ involvement that does not aid in establishing the diagnosis.
No comments:
Post a Comment