Research - Open Access
Laura Gochicoa-Rangel, Keylin Yaoska Rodríguez-Peralta, Ana Karen Gutiérrez-Bautista, Carlos Guzmán-Valderrábano, Rosario Fernández-Plata, Luis Torre-Bouscoulet & David Martínez-Briseño
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 22, Article number: 147 (2022)
Abstract
Background
Peak inspiratory and expiratory flows (PIF, PEF) are parameters used to evaluate the mechanics of the respiratory system. These parameters can vary based on whether they are measured using mechanical devices vs. spirometry and based on the barometric pressure at which the measurements are obtained. Our objectives were (1) to report the normal values and variability of PEF and PIF of a Latin American population living at a moderate altitude (2240 m above sea level), (2) to analyze the adjustment of reference values obtained at sea level with those obtained in healthy subjects living at a moderate altitude, and (3) to assess the correlation between PEF obtained by spirometry (PEFs) and PEF obtained by mechanical devices (PEFm).
Methods
In this prospective and transversal study, men and women with good respiratory health aged between 2.8 and 68 years old were invited to participate. Randomly, they underwent spirometry (to measure PEFs and PIFs) and mechanical flowmetry (to measure PEFm).
Results
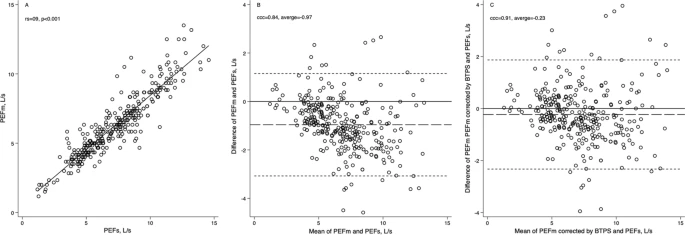
A total of 314 subjects participated, with an average age of 24.3 ± 16.4 years; 59% were Women. The main determinants for the reference equations were age, weight, height and sex at birth. The agreement of the PEFm, PEFs and PIFs values was inconsistent with that reported by other authors, even at the same barometric pressure. The association between PEFm and PEFs was r = 0.91 (p < 0.001), and the correlation coefficient of concordance was 0.84.
Conclusions
The PEFm, PEFs, and PIFs measurements in individuals living at moderate altitudes are different from those found by other authors in cities with different barometric pressures and ethnicities.
No comments:
Post a Comment