- Research
- Open access
Marwa G. Elhennawy, Yosri Akl, Nirmeen A. Sabry
BMC Pulmonary Medicine 24, Article number: 87 (2024)
Abstract
Purpose
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are caused by inflammation and/or fibrosis of alveolar walls resulting in impaired gas exchange. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is the third most common type of ILDs. Corticosteroids are the mainstay treatment for HP. The use of intramuscular (IM) betamethasone or intravenous (IV) dexamethasone as weekly pulse doses has shown higher benefit than daily oral prednisolone for HP patients. The aim of this study is to directly compare different corticosteroids in terms of effectiveness and in monetary values and perform an economic evaluation.
Methods
One hundred and seven patients were tested for pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and inflammatory markers to assess the treatment effectiveness.
A cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed. ICERs between 3 treatment groups were calculated.Results
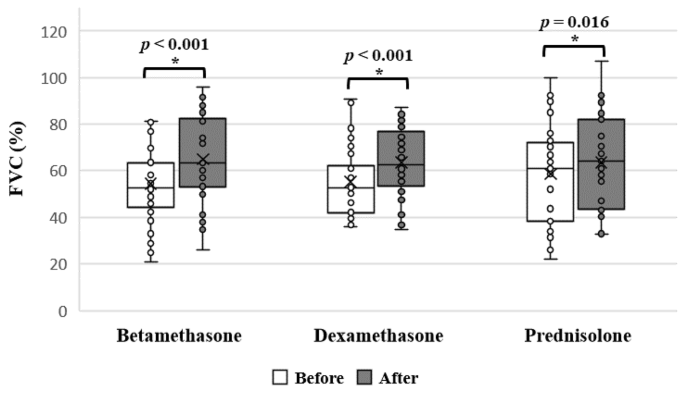 | |
Effect of using different corticosteroids on FVC
|
Conclusion
Betamethasone and dexamethasone were found to be more effective than prednisolone in improving the inflammatory reaction and the clinical features of HP patients. Betamethasone was found to be the best intervention in terms of cost against the effect.

No comments:
Post a Comment