Abstract
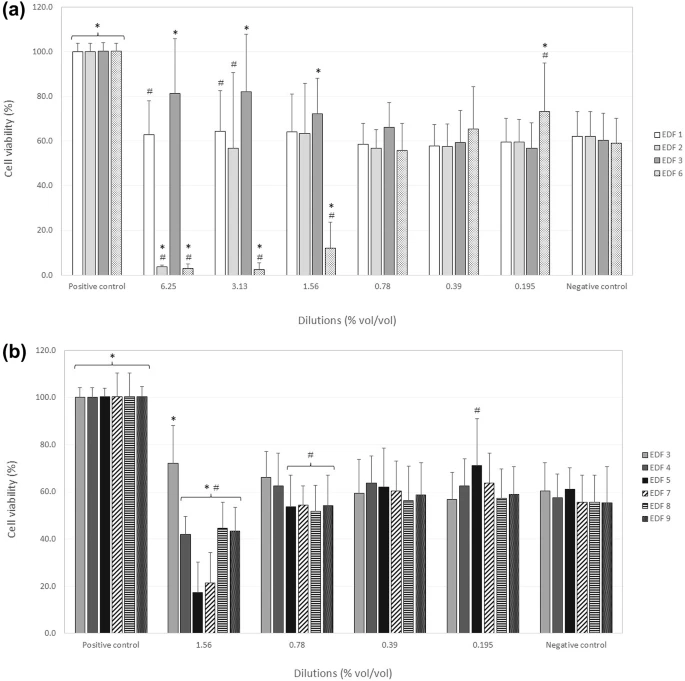 |
| Quantitative determination of the protective effect of selected antiallergic aye drop formulations against dehydration in Human Primary Conjunctival Epithelial Cells (HConEpiC) |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Abstract
 |
| Quantitative determination of the protective effect of selected antiallergic aye drop formulations against dehydration in Human Primary Conjunctival Epithelial Cells (HConEpiC) |
No comments:
Post a Comment