Copaescu, A.M., Chua, K.Y.L., Mouhtouris, E. et al. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 21, 35 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-025-00982-3
Abstract
Background
The use of in vivo and ex vivo diagnostic tools for delayed hypersensitivity reactions (DHRs) associated with iodinated contrast media (ICM) is currently ill-defined.
Objective
To evaluate the role of in vivo and ex vivo diagnostic tools for DHRs occurring >6 h following intravenous low-osmolality ICM.
Methods
We conducted a prospective, multicenter, international cohort study. The patients were recruited from two tertiary care adult allergy clinics, Austin Health, Australia and the McGill University Health Centre, Canada. Eligible participants were adults who reported a DHR after receiving ICM. In vivo testing (skin testing and intravenous challenge) was performed to identify an alternative agent. Ex vivo testing using interferon-γ enzyme-linked ImmunoSpot assay was performed in four Australian patients to explore its diagnostic performance.
Results
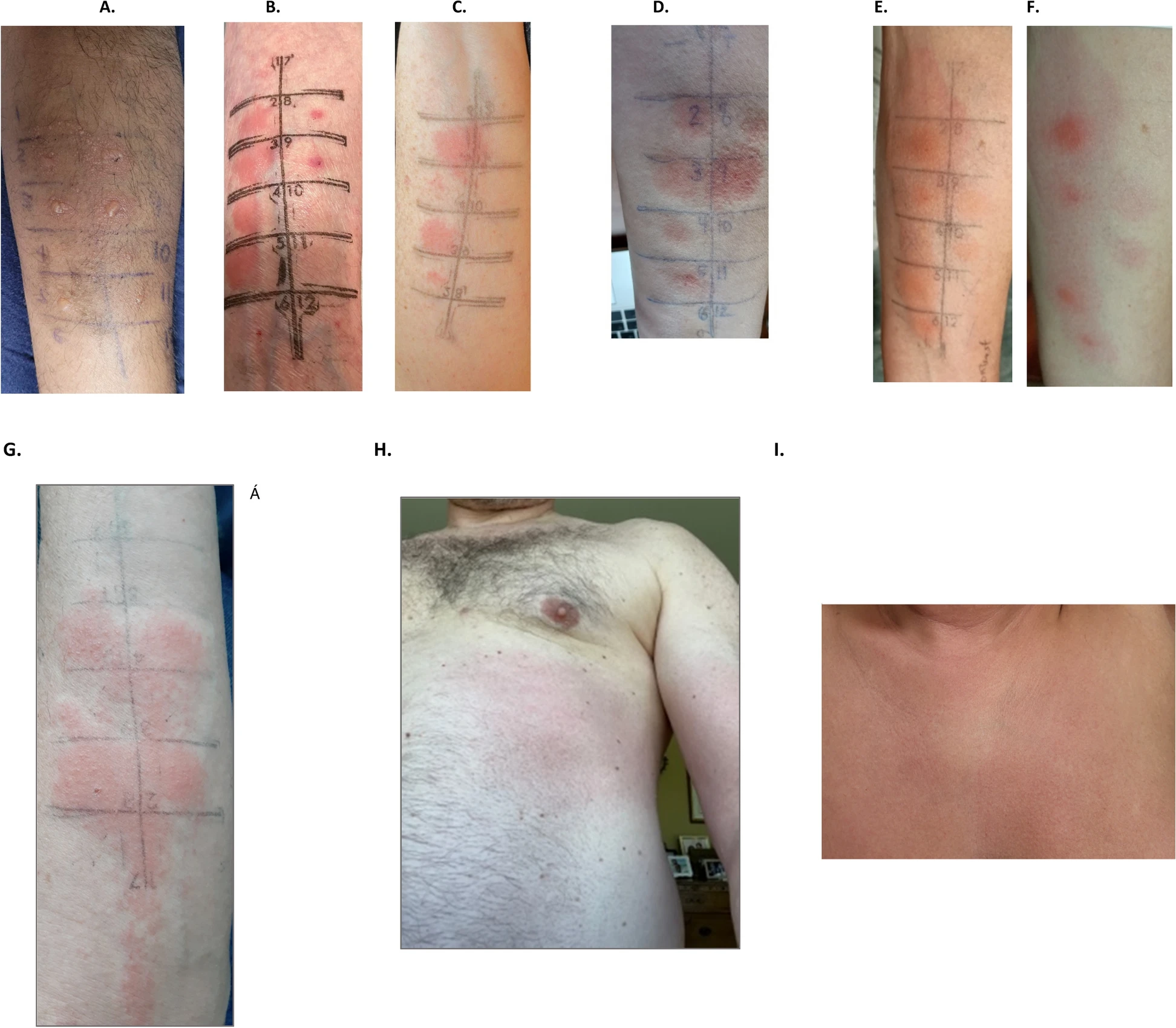 |
| Examples of delayed positive intradermal skin testing and intravenous challenges |
Conclusion
dIDT allowed confirmation of T cell mediated allergy to the implicated ICM in 85% of patients with a strong clinical suspicion of DHR and identification of non-cross-reactive ICM in 35% of patients. The IFN-y ELISpot was not useful in the four patients tested.

No comments:
Post a Comment