Wang, Z., Wang, N., Liang, X. et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-025-09664-7
Abstract
Introduction
Reappraisal of Systematic reviews/Meta analyses on Sublingual Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis: Evidence for Clinical Practice and Decision-Making.
Methods
A comprehensive computerized search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, VIP, WANFANG, and CBM databases from their inception to June 8, 2025, to systematically identify Systematic reviews and Meta analyses on Sublingual Immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. A citation overlap matrix was constructed to calculate the corrected covered area, assessing the degree of primary study overlap. The risk of bias, methodological quality, reporting quality, and certainty of evidence in the included Systematic reviews/Meta analyses were evaluated using ROBIS, AMSTAR-2, PRISMA 2020, and GRADE tools, respectively. Both quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed on the primary outcomes to derive a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding.
Results
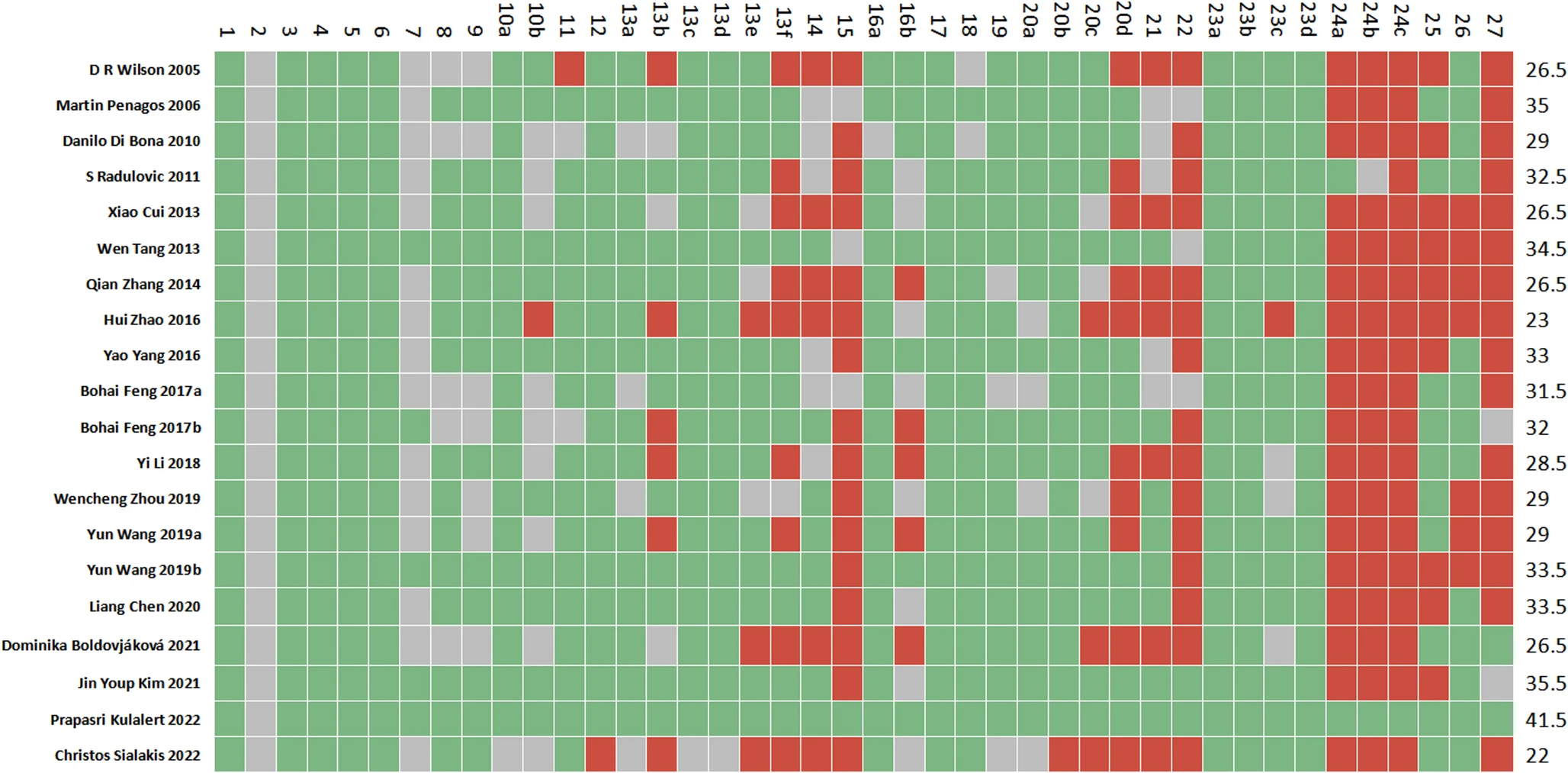 |
| Cartesian heatmap of the scores of each item in PRISMA 2020. Note: Green indicates compliance; Gray indicates partial compliance; Red indicates non-compliance |
Discussion
Current evidence demonstrates that Sublingual Immunotherapy exhibits favorable efficacy in improving symptom scores and medication use for allergic rhinitis, with generally acceptable safety profiles despite mild adverse reactions in some cases. Future research should focus on large-scale, real-world studies with diverse outcome measures, investigating variations in regional populations, allergen types, dosage regimens, and treatment durations to further optimize clinical application protocols for Sublingual Immunotherapy.

No comments:
Post a Comment