Kelsen, S.G., Maurer, M., Waters, M. et al. Respir Res 26, 302 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-025-03360-0
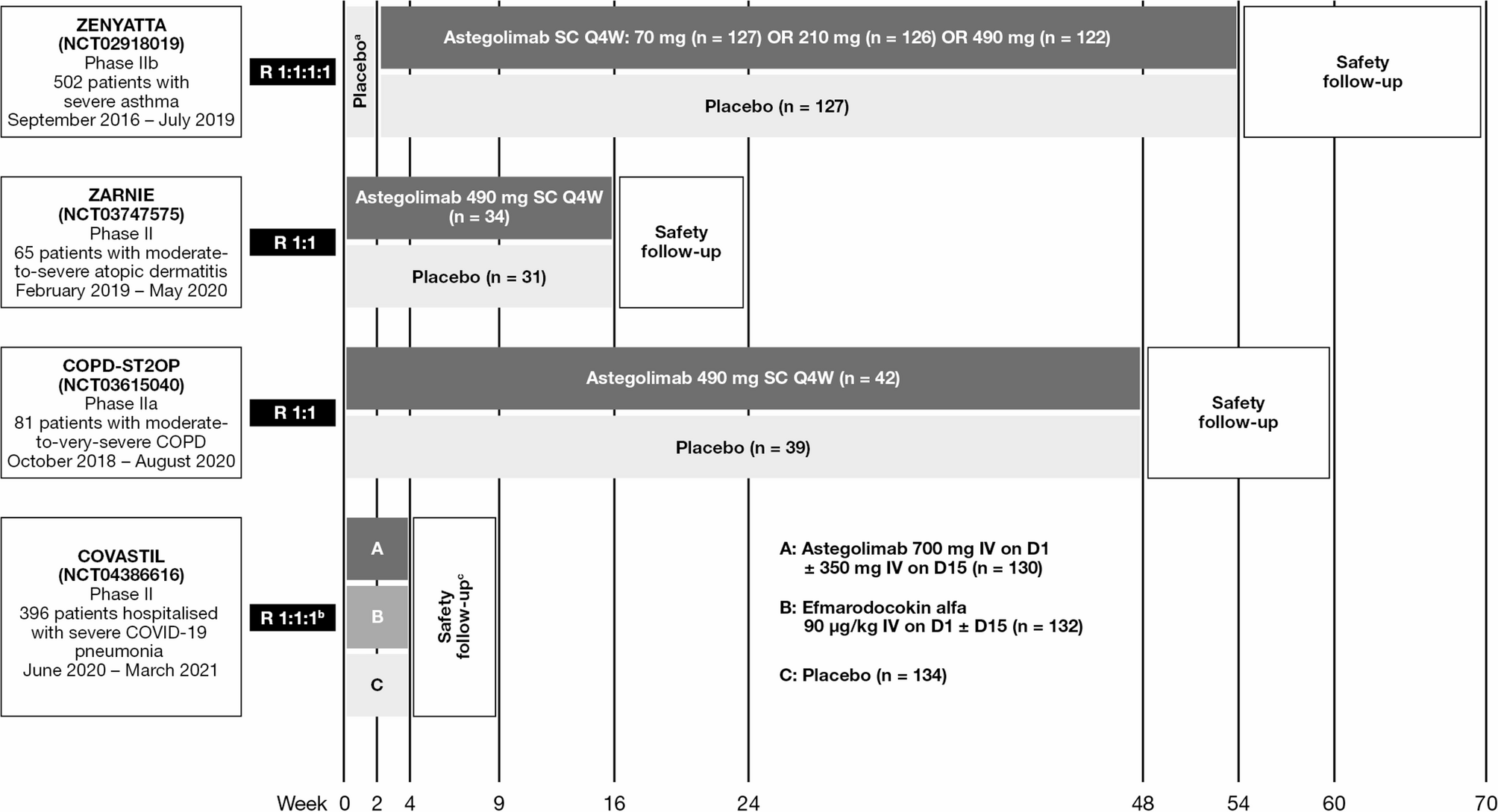 |
| An overview of published randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase II/IIa/IIb trials of astegolimab |
Abstract
Chronic inflammation is an underlying feature of respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Novel therapies that target the inflammatory mechanisms driving acute exacerbations of COPD are required. The ST2 receptor, which binds the alarmin interleukin (IL)-33 to initiate an inflammatory response, is a potential target. Astegolimab, a fully human immunoglobulin G2 monoclonal antibody, which binds with high affinity to ST2 to prevent binding of IL-33, is a potential therapy for COPD. However, targeting inflammatory pathways that form part of the immune system may have unintended consequences, such as implications for the response to infection and cardiovascular function. Therefore, an understanding of astegolimab’s safety profile in clinical use is essential.
This narrative review summarizes clinical safety data from published clinical trials of astegolimab with a focus on adverse events of interest, including infections and cardiac events.
Astegolimab was shown to be well tolerated in > 580 patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, COPD, and severe COVID-19 pneumonia who took part in Phase II trials. The frequency of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs was similar between the astegolimab and placebo arms in each trial (AEs: 41–81% vs. 58–77%; serious AEs: 3–29% vs. 0–41%, respectively). The number of deaths was similar between treatment arms and there were no astegolimab-related deaths. Astegolimab did not increase the risk of infection or major adverse cardiac events. Ongoing Phase IIb and Phase III trials of astegolimab in patients with COPD who have a history of frequent acute exacerbation(s) of COPD will provide a future opportunity to confirm the safety profile of astegolimab.
Chronic inflammation is an underlying feature of respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Novel therapies that target the inflammatory mechanisms driving acute exacerbations of COPD are required. The ST2 receptor, which binds the alarmin interleukin (IL)-33 to initiate an inflammatory response, is a potential target. Astegolimab, a fully human immunoglobulin G2 monoclonal antibody, which binds with high affinity to ST2 to prevent binding of IL-33, is a potential therapy for COPD. However, targeting inflammatory pathways that form part of the immune system may have unintended consequences, such as implications for the response to infection and cardiovascular function. Therefore, an understanding of astegolimab’s safety profile in clinical use is essential.
This narrative review summarizes clinical safety data from published clinical trials of astegolimab with a focus on adverse events of interest, including infections and cardiac events.
Astegolimab was shown to be well tolerated in > 580 patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, COPD, and severe COVID-19 pneumonia who took part in Phase II trials. The frequency of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs was similar between the astegolimab and placebo arms in each trial (AEs: 41–81% vs. 58–77%; serious AEs: 3–29% vs. 0–41%, respectively). The number of deaths was similar between treatment arms and there were no astegolimab-related deaths. Astegolimab did not increase the risk of infection or major adverse cardiac events. Ongoing Phase IIb and Phase III trials of astegolimab in patients with COPD who have a history of frequent acute exacerbation(s) of COPD will provide a future opportunity to confirm the safety profile of astegolimab.
No comments:
Post a Comment