- Review
- Open Access
Abstract
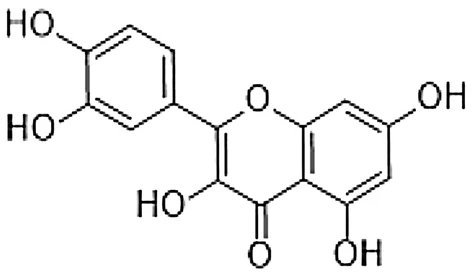
Quercetin is a naturally occurring polyphenol flavonoid which is rich in antioxidants. It has anti-allergic functions that are known for inhibiting histamine production and pro-inflammatory mediators. Quercetin can regulate the Th1/Th2 stability, and decrease the antigen-specific IgE antibody releasing by B cells. Quercetin has a main role in anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory function which makes it proper for the management of different diseases.