Maniscalco M, Detoraki A, Sarnelli G, Nolano M, De Paulis A, Spadaro G, Cantone E;
J Pers Med. 2023 Jun 1;13(6):941. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060941.Open AccessEditorial
Patients with atopic/allergic disorders, including atopic dermatitis (AD), allergic rhino-conjunctivitis (AR), chronic rhinosinusitis with/without nasal polyps (CRSwNP/CRSsNP), bronchial asthma, food allergy, and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), often share a common genetic background, a type Th2 polarized immune response, and several environmental factors.
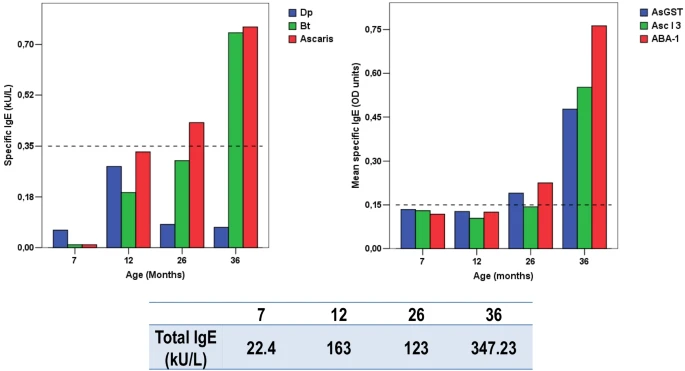
Th2 immunity has evolved to ensure the integrity of the epithelial barrier and to protect against helminths.