- Letter to the editor
- Open Access
- Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology
Abstract
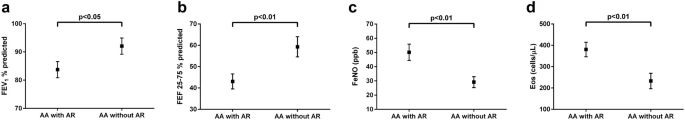
The concept of the unified allergic airway disease (UAD) recognises the association between allergic inflammation in the upper and lower airways. Patients with asthma and concomitant allergic rhinitis experience more asthma-related primary and secondary care visits. We therefore aimed to determine differences in asthma control (asthma control questionnaire ACQ-6), lung function (spirometry) and T2 biomarkers (FeNO and Eos) in relation to the presence of allergic rhinitis in patients with allergic asthma.