A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
May 28, 2020
Male sex is strongly associated with IgE-sensitization to airborne but not food allergens: results up to age 24 years from the BAMSE birth cohort
Abstract
Background
Up to half of the population in high-income countries has allergen-specific IgE antibodies. However, data regarding sex differences of IgE-sensitization from childhood to adulthood is limited.
May 27, 2020
Visit EAACI Digital Congress 2020 with us!
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
|
May 25, 2020
Concordance for changes in allergic asthma domain variables after short-term corticosteroid therapy
Research article - Open Access
BMC Pulmonary Medicine
Philip E. Silkoff, Mark Sarno, Solomon Ssenyange, Vivek Balasubramanyam, Brian Awabdy & Ryan Leard
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 20, Article number: 139 (2020)
Abstract
Background
Asthma is a complex syndrome with multiple domains including symptoms, lung function, asthma control, and airway inflammation. A study of Fenom PRO™, a novel monitor for exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), provided an opportunity to look at concordance/discordance (C/D) for changes in multiple asthma domains over a 2-week period after corticosteroid therapy.
Methods
Non-steroid-treated adults and children with uncontrolled asthma had asthma domain measures, (FeNO), forced expired volume in 1 s (FEV1), the 6-item Asthma Control Questionnaire scores (ACQ6), and daily asthma symptoms, assessed before and after a 2-week course of corticosteroids.
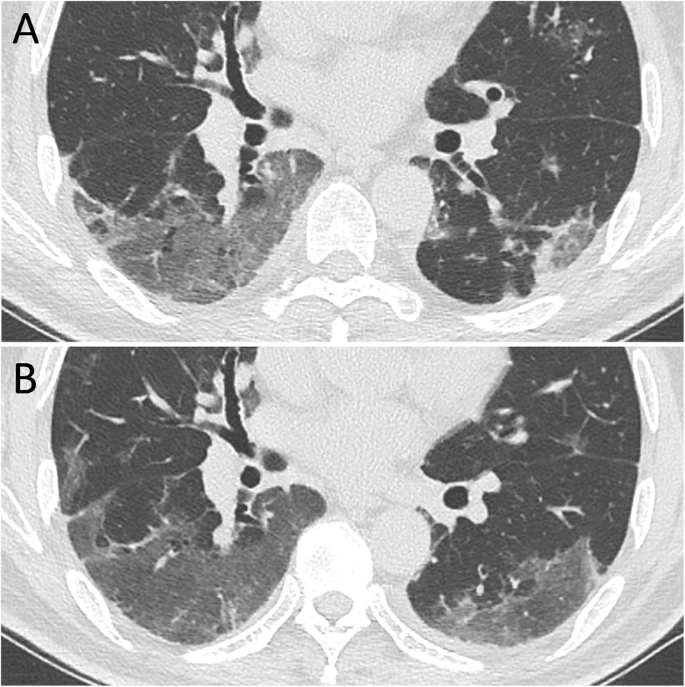
The pulmonary sequalae in discharged patients with COVID-19: a short-term observational study
Respiratory Research Research- Open Access
Dehan Liu, Wanshu Zhang, Feng Pan, Lin Li, Lian Yang, Dandan Zheng, Jiazheng Wang & Bo Liang Respiratory Research volume 21, Article number: 125 (2020)
Dehan Liu, Wanshu Zhang, Feng Pan, Lin Li, Lian Yang, Dandan Zheng, Jiazheng Wang & Bo Liang Respiratory Research volume 21, Article number: 125 (2020)
Abstract
Background
A cluster of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia were discharged from hospitals in Wuhan, China. We aimed to determine the cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution at each time point, to explore the relevant affecting factors, and to describe the chest CT findings at different time points after hospital discharge.
Methods
Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia confirmed by RT-PCR who were discharged consecutively from the hospital between 5 February 2020 and 10 March 2020 and who underwent serial chest CT scans on schedule were enrolled.
Background
A cluster of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia were discharged from hospitals in Wuhan, China. We aimed to determine the cumulative percentage of complete radiological resolution at each time point, to explore the relevant affecting factors, and to describe the chest CT findings at different time points after hospital discharge.
Methods
Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia confirmed by RT-PCR who were discharged consecutively from the hospital between 5 February 2020 and 10 March 2020 and who underwent serial chest CT scans on schedule were enrolled.
May 23, 2020
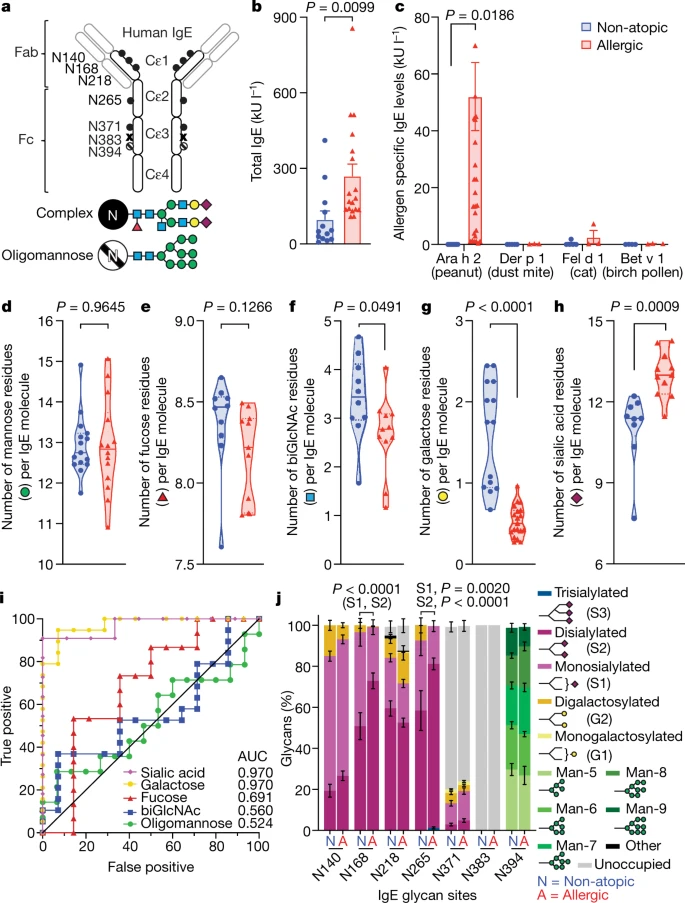
Sialylation of immunoglobulin E is a determinant of allergic pathogenicity
Abstract
Approximately one-third of the world’s population suffers from allergies1. Exposure to allergens crosslinks immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies that are bound to mast cells and basophils, triggering the release of inflammatory mediators, including histamine2. Although IgE is absolutely required for allergies, it is not understood why total and allergen-specific IgE concentrations do not reproducibly correlate with allergic disease3,4,5. It is well-established that glycosylation of IgG dictates its effector function and has disease-specific patterns. However, whether IgE glycans differ in disease states or affect biological activity is completely unknown6. Here we perform an unbiased examination of glycosylation patterns of total IgE from individuals with a peanut allergy and from non-atopic individuals without allergies.
May 20, 2020
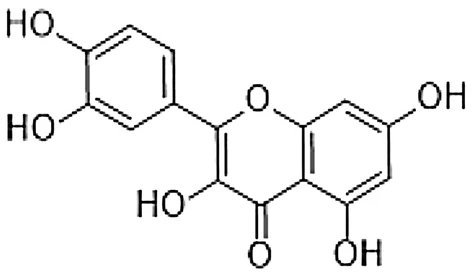
Quercetin with the potential effect on allergic diseases
- Review
- Open Access
Abstract
Quercetin is a naturally occurring polyphenol flavonoid which is rich in antioxidants. It has anti-allergic functions that are known for inhibiting histamine production and pro-inflammatory mediators. Quercetin can regulate the Th1/Th2 stability, and decrease the antigen-specific IgE antibody releasing by B cells. Quercetin has a main role in anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory function which makes it proper for the management of different diseases.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)