Adherence to inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in asthma is vital for disease control. However, obtaining reliable and clinically useful measures of adherence remains a major challenge. We investigated the association between patient-reported adherence and objectively measured adherence based on filled prescriptions with inhaled corticosteroids in adults with asthma.
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
June 6, 2021
June 3, 2021
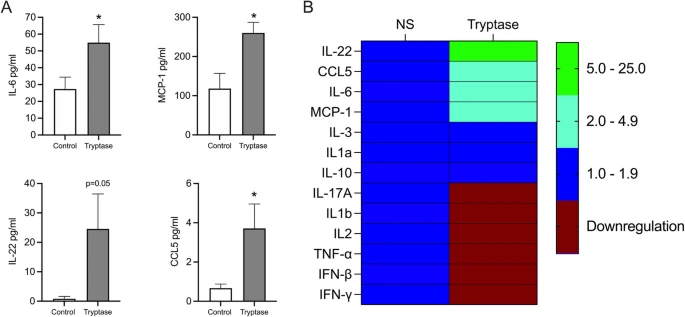
Direct effects of mast cell proteases, tryptase and chymase, on bronchial epithelial integrity proteins and anti-viral responses
- Research article
- Open Access
Mast cells (MCs) are known to contribute to both acute and chronic inflammation. Bronchial epithelial cells are the first line of defence against pathogens and a deficient anti-viral response has been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of asthma exacerbations. However, effects of MC mediators on bronchial epithelial immune response have been less studied. The aim of this study is to investigate the direct effects of stimulation with MC proteases, tryptase and chymase, on inflammatory and anti-viral responses in human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs).
May 30, 2021
Small airway dysfunction and poor asthma control: a dangerous liaison
- Review
- Open Access
Clinical and Molecular Allergy volume 19, Article number: 7 (2021)
Asthma is a common chronic condition, affecting approximately 339 million people worldwide. The main goal of the current asthma treatment guidelines is to achieve clinical control, encompassing both the patient symptoms and limitations and the future risk of adverse asthma outcomes. Despite randomized controlled trials showing that asthma control is an achievable target, a substantial proportion of asthmatics remain poorly controlled in real life.
May 8, 2021
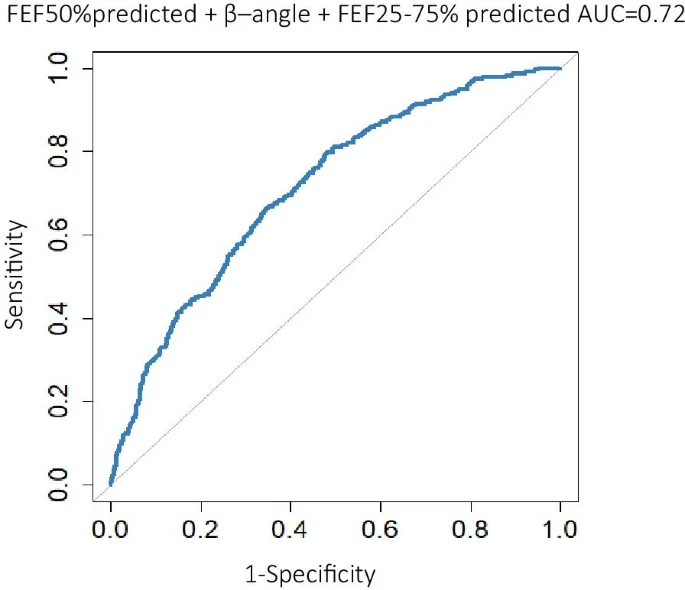
Baseline spirometry parameters as predictors of airway hyperreactivity in adults with suspected asthma
April 22, 2021
Trained immunity induced by in vivo peptide-based STAT6 inhibition prevents ragweed allergy in mice
Trained immunity is the ability of the innate immune system to form immune memory responses to provide support the formation of appropriate adaptive responses. Allergic airways disease (AAD) is a maladapted immune response to allergens, initiated and maintained by the type 2 (T2) inflammatory pathway. It is predicated by the elaboration of cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 and follows activation of the STAT6 transcription factor.
April 21, 2021
Leveraging unstructured data to identify hereditary angioedema patients in electronic medical records
- Research
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 17, Article number: 41 (2021)
The epidemiologic impact of hereditary angioedema (HAE) is difficult to quantify, due to misclassification in retrospective studies resulting from non-specific diagnostic coding. The aim of this study was to identify cohorts of patients with HAE-1/2 by evaluating structured and unstructured data in a US ambulatory electronic medical record (EMR) database.
April 18, 2021
Effectiveness of a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia in the elderly with chronic respiratory diseases: a case–control study of a single center
- Research
- Open Access
- Toshihiro Masuda,
- Eiji Nakatani,
- Toshihiro Shirai,
- Taisuke Akamatsu,
- Kanami Tamura,
- Shingo Takahashi,
- Yuko Tanaka,
- Hirofumi Watanabe,
- Yoshinari Endo,
- Takahito Suzuki,
- Mika Saigusa,
- Akito Yamamoto,
- Satoru Morita,
- Yoko Sato &
- Kazuhiro Asada
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 21, Article number: 123 (2021)
The effectiveness of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) in preventing pneumococcal pneumonia has been controversial.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the PPSV23 in elderly outpatients with chronic respiratory diseases, we carried out a case–control study, including 4128 outpatients aged ≥ 65 years, in the respiratory department.
April 14, 2021
H2-antagonist in IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity reactions: what literature says so far?
- Clinical and Molecular Allergy
- Letters to the Editor
- Open Access
Clinical and Molecular Allergy volume 19, Article number: 4 (2021)
Abstract
Histamine is a monoamine synthesized from the amino acid histidine that is well-known for its role in IgE-mediated anaphylaxis but has shown pleiotropic effects on the immune system, especially in order to promote inflammatory responses. H1-receptor antagonist are common drugs used in mild/moderate allergic reactions whereas H2-receptor antagonist are commonly administered in gastric ulcer but showed some properties in allergy too. The EAACI guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of anaphylactic reactions recommend their use as third-line therapy in adjunct to H1-antagonists. The purpose of this article is to produce a complete summary of findings and evidence known so far about the usefulness of H2-receptor antagonist in allergic reactions.