- Research
- Open Access
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
November 30, 2021
Interleukin-22 attenuates allergic airway inflammation in ovalbumin-induced asthma mouse model
November 29, 2021
Volatile organic breath components and exercise induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic children
- Research
- Open Access
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 17, Article number: 121 (2021)
November 20, 2021
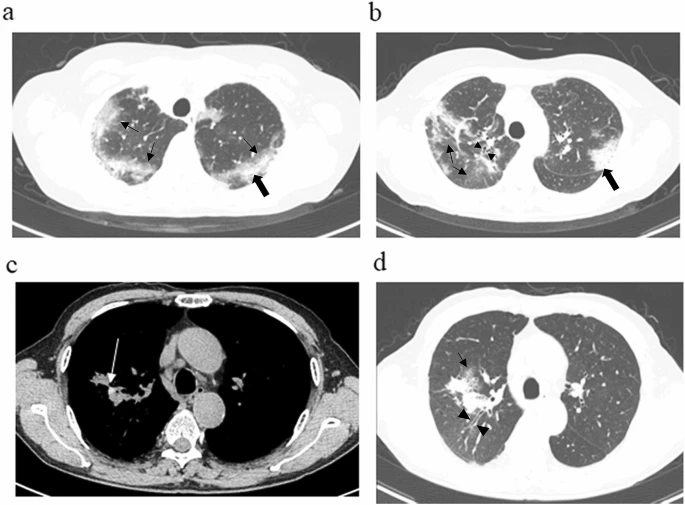
Pulmonary eosinophilia may indicate onset stage of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Research
- Open Access
- Mari Miki,
- Yuko Ohara,
- Kazuyuki Tsujino,
- Takahiro Kawasaki,
- Tomoki Kuge,
- Yuji Yamamoto,
- Takanori Matsuki,
- Keisuke Miki &
- Hiroshi Kida
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 17, Article number: 118 (2021)
Abstract
Background
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) both display peripheral eosinophilia as well as pulmonary infiltration, together described as pulmonary eosinophilia, and differentiation is sometimes problematic. This study therefore examined the distinctions between ABPA with and without CEP-like shadows.
November 18, 2021
Differential uptake of three clinically relevant allergens by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- Research
- Open Access
- Noelle Zurmühl,
- Anna Schmitt,
- Ulrike Formentini,
- Johannes Weiss,
- Heike Appel,
- Klaus-Michael Debatin &
- Dorit Fabricius
Clinical and Molecular Allergy volume 19, Article number: 23 (2021)
Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) have a dual role as interferon-producing and antigen-presenting cells. Their relevance for allergic diseases is controversial. and the impact of pDC on allergic immune responses is poorly understood.
November 13, 2021
Induction of remission in chronic urticaria by immunotherapy using immunoglobulin/histamine complex (Histobulin™): a case report
- Case Report
- Open Access
- Published:
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology volume 17, Article number: 116 (2021)
Symptom control is a major concern in chronic urticaria. Histobulin™ is a histamine/immunoglobulin complex that has been approved for allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma and chronic urticaria in some countries. Not only has the immunoglobulin/histamine complex been reported to be effective in allergic diseases, including chronic urticaria, but recently, the possibility of remission induction in chronic urticaria by the immunoglobulin/histamine complex has been reported.
November 5, 2021
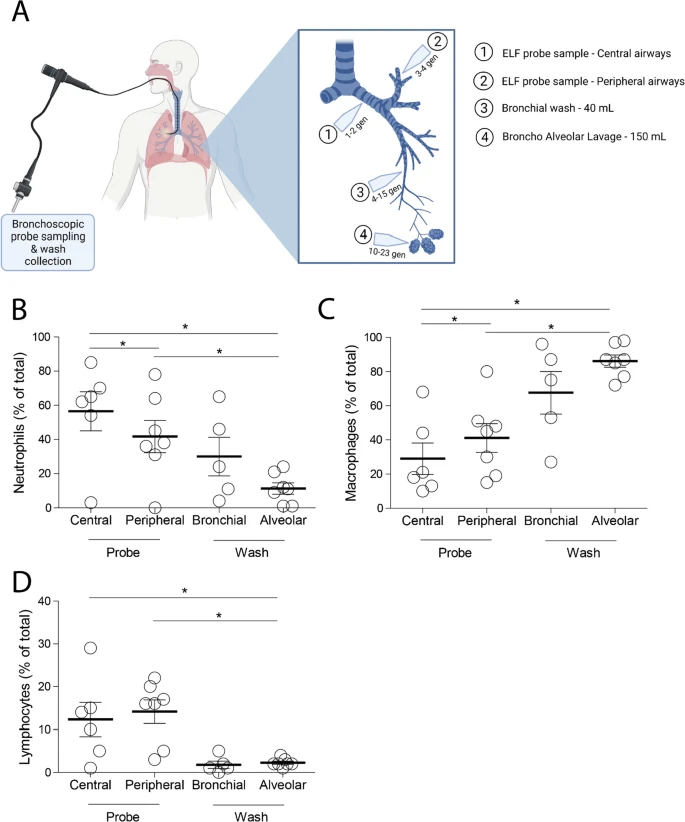
The cellular composition of the lung lining fluid gradually changes from bronchus to alveolus
- Letter to the Editor
- Open Access
Abstract
Although large advances have recently been made mapping out the cellular composition of lung tissue using single cell sequencing, the composition and distribution of the cellular elements within the lining fluid of the lung has not been extensively studied. Here, we assessed the cellular composition of the lung lining fluid by performing a differential cell analysis on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and epithelial lining fluid (ELF) at four different locations within the lung in post-lung transplantation patients. The percentage of neutrophils and lymphocytes is reduced in more distal regions of the lungs, while the percentage of macrophages increases in these more distal regions.
October 29, 2021
Long-term predictors of severe exacerbations and mortality in a cohort of well-characterised adults with asthma
- Research
- Open Access
Respiratory Research volume 22, Article number: 269 (2021)
We aimed to explore long-term predictors of severe exacerbations and mortality in adults with well-characterised asthma.
October 27, 2021
Association between particulate matter containing EPFRs and neutrophilic asthma through AhR and Th17
- Respiratory Research
- Open Access
Epidemiological data associate high levels of combustion-derived particulate matter (PM) with deleterious respiratory outcomes, but the mechanism underlying those outcomes remains elusive. It has been acknowledged by the World Health Organization that PM exposure contributes to more than 4.2 million all-cause mortalities worldwide each year. Current literature demonstrates that PM exacerbates respiratory diseases, impairs lung function, results in chronic respiratory illnesses, and is associated with increased mortality.