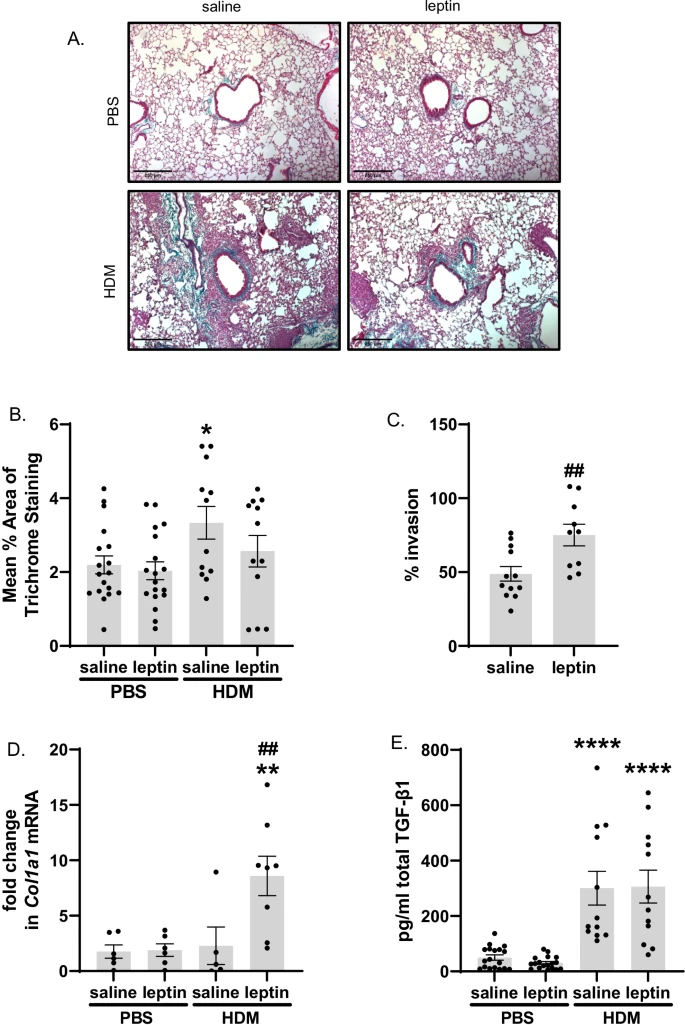
Background
Asthma patients with comorbid obesity exhibit increased disease severity, in part, due to airway remodeling, which is also observed in mouse models of asthma and obesity. A mediator of remodeling that is increased in obesity is leptin. We hypothesized that in a mouse model of allergic airways disease, mice receiving exogenous leptin would display increased airway inflammation and fibrosis.
Methods
Five-week-old male and female C57BL/6J mice were challenged with intranasal house dust mite (HDM) allergen or saline 5 days per week for 6 weeks (n = 6–9 per sex, per group). Following each HDM exposure, mice received subcutaneous recombinant human leptin or saline.