Muñoz, M., Kiefer, L.A., Pereira, M.P. et al. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-024-01160-y
Abstract
Purpose of Review
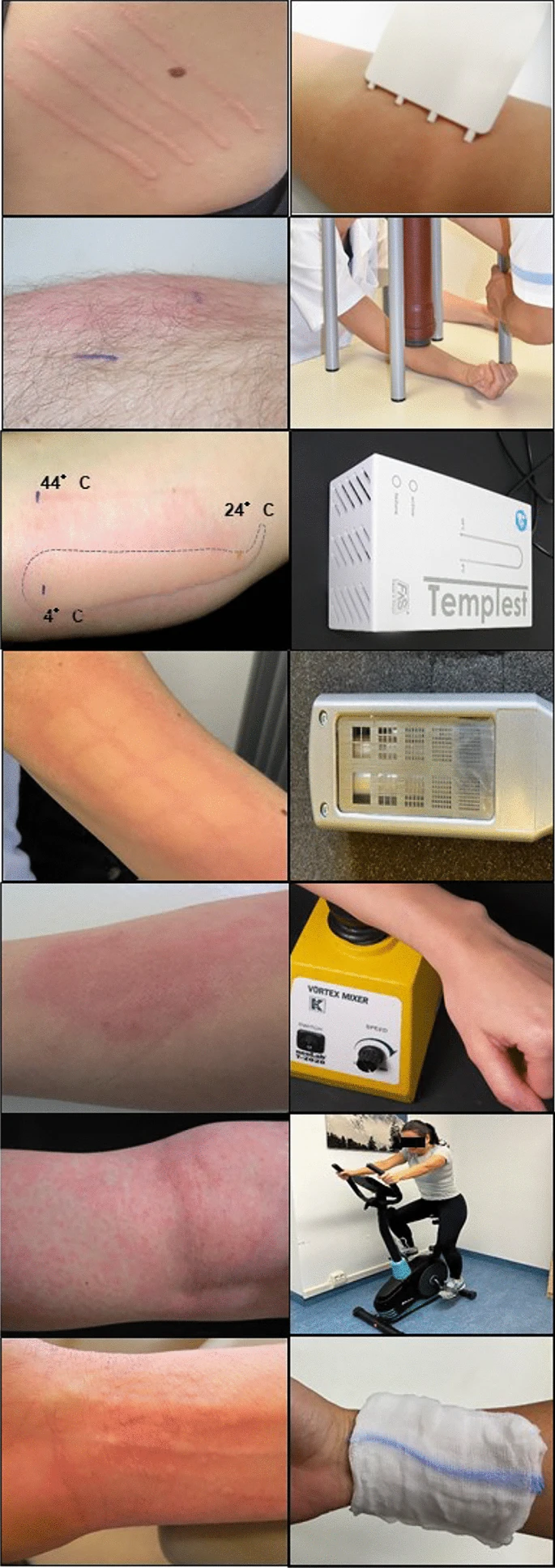
Chronic inducible urticaria (CIndU) is a group of long-persisting and challenging to manage diseases, characterized by recurrent wheals and angioedema induced by definite triggers. In this review, we address recent findings on CIndU pathogenesis, diagnosis as well as its treatment, and we discuss novel potential targets that may lead to the development of more effective therapies for CIndU patients.
Recent Advances
Meaningful advances in the understanding of its pathogenesis have been reported in the last decades. Novel CIndU-specific patient-reported outcome measures enable a closer and better evaluation of patients.
Summary
CIndU is a hard-to-treat disease that highly impairs quality of life (QoL) of affected patients. Provocation tests allow to diagnose CIndU subtypes. The only licensed and recommended treatment for CIndU are second generation non-sedating H1-antihistamines, which lack efficacy in many cases. Omalizumab off-label use has been assessed in all types of CIndU with overall good outcomes. Promising emerging therapies currently assessed in chronic spontaneous urticaria are paving the path for novel treatments for CIndU.