Holze, J., Lauber, F., Soler, S. et al. Nat Commun 15, 9554 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53770-9
Abstract
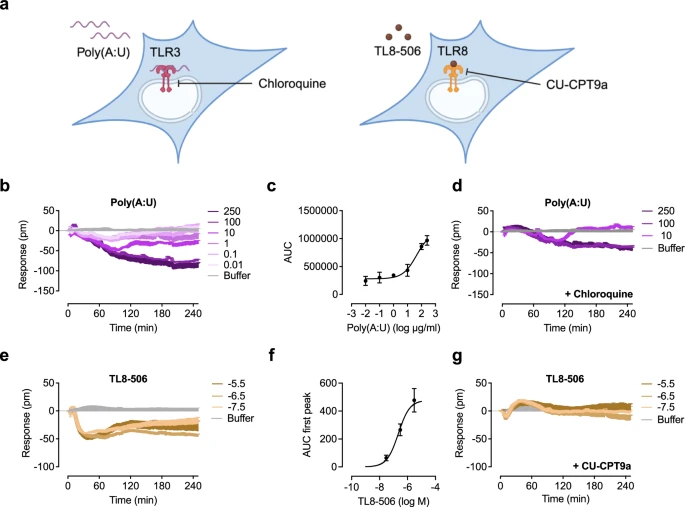 |
| Optical biosensor decodes signaling of endosomal TLRs. |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Holze, J., Lauber, F., Soler, S. et al. Nat Commun 15, 9554 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53770-9
Abstract
 |
| Optical biosensor decodes signaling of endosomal TLRs. |
Frias Sartorelli de Toledo Piza C, Aranda CS, Solé D, Jolles S, Condino-Neto A. Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1495564. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1495564.
Abstract
Purpose: Calculated globulin (CG, total protein minus albumin levels) correlate well with IgG levels and has been proposed as a suitable screening method for individuals with primary antibody deficiencies (PADs). We aimed to show the correlation of CG with IgG levels in children and adolescents, utilizing a common method for albumin measurement, bromocresol green.
Methods: Individuals from two Allergy and Immunology clinics were invited to participate. Inclusion criteria were age < 18, stable conditions, and signed informed consent. We included 1084 individuals. Immunoglobulin G values were determined by immunoturbidimetry; the colorimetric bromocresol green method and the Architect Biuret method were utilized for the albumin and total protein (TP) measurements, respectively.
Abstract
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der p) subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) has demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials of childhood allergic rhinitis (AR). Currently, there is a lack of some generally accepted biomarkers that may predict the clinical response to SCIT to eventually achieve personalized therapy. In this study, 28 children with AR received Der p SCIT for 26–30 months at baseline, and four efficacy endpoints, serum interleukin (IL)-5, periostin, Der p-specific IgE (sIgE), and Der p sIgG4, were measured by ELSIA. Clinical symptoms and characteristics were assessed by questionnaires, and the associations among periostin, Der p 2 sIgE and clinical efficacy were analyzed. The results showed that SCIT demonstrated a significant reduction in Der p 1 sIgE (P < 0.05) and Der p 2 sIgE (P < 0.01), an increase in Der p sIgG4 (P < 0.001) and an improvement in clinical efficacy at the fourth efficacy endpoint compared with that at baseline.
 |
| Correlations between the changes in clinical indices in childhood with AR treatment with SCIT. |
Abstract
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergies are the most common type of food allergy, often causing rapid symptoms after exposure to allergens posing a serious health risk and a high impact on patient's and caregiver's quality of life. Omalizumab, a humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody, reduces allergic reactions by binding to circulating IgE. Omalizumab has been successfully used in allergic asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and chronic urticaria, and was recently approved for treating IgE-mediated food allergies by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
This GA2LEN ANACARE Consensus Statement presents our position on the use of omalizumab for treating IgE-mediated food allergies, based on a systematic review and meta-analysis, experience with use for other conditions, and expert consensus achieved via an eDelphi process.Dear Friends & Colleagues,
We invite you to attend an ARIA webinar entitled ARIA GUIDELINES 2024
DATE: Tuesday 19 November
TIME: 18.00 - 19.00 CET (France time zone)
AGENDA :
Jean Bousquet: Overall presentation of the ARIA Guidelines
Bernardo Sousa Pinto: Artificial Intelligence in ARIA Guidelines and Evidence to Decision
To join the webinar, please click here
For those who cannot join on Tuesday > we will be having a repeat webinar (exactly the same) before the end of the month.
We look forward to seeing you there
Best wishes
Jean, Bernardo, Anna, Veronique
Laikitmongkhon, J., Tassaneyasin, T., Sutherasan, Y. et al. BMC Pulm Med 24, 562 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-024-03364-4
Abstract
Background
The most appropriate anti-inflammatory treatment for moderate COVID-19 pneumonia remains uncertain. We aimed to compare the effectiveness of a high-dose methylprednisolone versus a high-dose dexamethasone in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 pneumonia, regarding the WHO clinical progression scales, mortality, and the length of hospitalization.
Methods
In this open-labeled randomized controlled trial, we enrolled patients with age > 18 years old who were diagnosed moderate COVID-19 pneumonia confirmed by real-time PCR, evidence of pneumonia by chest imaging and resting oxygen saturation between 90 and 94%. Patients were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive methylprednisolone 250 mg/day or dexamethasone 20 mg/day over the first three days.
Solé D, Kuschnir FC, Pastorino AC et al. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Sep 7;91(1):101500. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101500.
Highlights
• This consensus brings together the most up-to-date information on rhinitis.
• Anamnesis is the key point in the suspected diagnosis and phenotype identification.
• It is especially important to recognize comorbidities.
• One aspect that impacts adequate treatment is low patient compliance.
Abstract
Since we published the “IV Brazilian Consensus on Rhinitis”, in 2017, several advances have been achieved and have enabled a further understanding of the different aspects of “Rhinitis”. This new guideline, developed jointly by ASBAI, SBP and SBORL, represents a relevant milestone in the updated and integrated management of the different forms of the disease, and it aims to unify evidence-based approaches to improve the diagnosis and treatment of this common and often underestimated condition. The document covers a wide range of topics, including clear definitions of the different phenotypes and endotypes of rhinitis, risk factors, updated diagnostic criteria, and recommended methods for clinical and laboratory investigation.
Amal Isaiah, Sophia Uddin, Thomas Ernst, Christine Cloak, Dongdong Li, Linda Chang. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(11):e2444057. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.44057
Key Points
Question Is parent-reported snoring frequency associated with cognitive and behavioral outcomes in adolescents?
Findings In this cohort study of 11 862 adolescents, frequent snoring was associated with greater problem behaviors but not with lower cognition.
Meaning These findings suggest that clinicians should incorporate the differential associations of snoring with cognitive and behavioral outcomes in shared decision-making concerning the management of adolescents with sleep-disordered breathing symptoms.
Abstract
Importance Snoring is central to sleep-disordered breathing (SDB), which arises from nocturnal upper airway resistance. Habitual snoring is associated with cognitive and behavioral problems in young children, but less is known about these associations in adolescents.
Objective To assess the longitudinal associations of snoring with cognition and problem behaviors among adolescents.