Abstract
 |
| The comparison of medications used by participants versus medications recommended by guidelines appropriate for the participants’ AR status (n = 167). |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
Abstract
 |
| The comparison of medications used by participants versus medications recommended by guidelines appropriate for the participants’ AR status (n = 167). |
Batard, T., Taillé, C., Guilleminault, L., Bozek, A., Floch, V.-L., Pfaar, O., Canonica, W., Akdis, C., Shamji, M. and Mascarell, L. (2024) Clin Exp Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.14575
ABSTRACT
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
Sladek S, Unger-Manhart N, Siegl C et al. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024;18:2797-2811 https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S476163
Abstract:
Purpose: This randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover, double‐blind trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tacrosolv, a novel 0.005% tacrolimus eye-drop solution, in adults with grass pollen–induced allergic conjunctivitis.
Methods: A total of 64 adult participants were randomized to receive 2.5 μg or 5 μg tacrolimus/eye/day or placebo treatment for 8 days, with grass pollen exposure on day 1 and day 8. After a 2-week washout period, placebo participants crossed over to Tacrosolv treatment and vice versa, with repeated treatment and exposure. During exposure, participants recorded ocular, nasal, and respiratory allergy symptoms every 15 minutes. The primary endpoint was the mean total ocular symptom score (TOSS) on day 8. Objective ocular safety parameters were assessed before, during, and after exposure. Adverse events were recorded throughout the study.
 |
| Comparison of wheat and ω-5 gliadin sIgE levels between the WA and NWA groups. |
Abstract
Allergic disease is caused by the activation of allergen-specific CD4+ type-2 T follicular helper cells (Tfh2) and T helper 2 (Th2) effector cells that secrete the cytokines IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13 upon allergen encounter, thereby inducing IgE production by B cells and tissue inflammation. While it is accepted that the priming and differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th2 requires allergen presentation by type 2 dendritic cells (DC2s), the underlying signals remain unidentified.
 |
| Allergen sensing by dendritic cells (DCs). |
![]() Zhu LL, Wang YH, Feng JH, Zhou Q. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:4387-4399 https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S484897
Zhu LL, Wang YH, Feng JH, Zhou Q. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:4387-4399 https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S484897
Background: Bacterial lysates are known for having immunomodulatory properties and have been used mainly for the prevention and treatment of respiratory tract infections (RTIs). However, rigorous studies are needed to confirm the clinical efficacy of bacterial lysates with various bacterial antigen components, preparation methods, administration routes and course of treatment. OM-85, an oral standardized lysate prepared by alkaline lysis of 21 strains from 8 species of common respiratory tract pathogens, is indicated as immunotherapy for prevention of recurrent RTIs and acute infectious exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. OM-85 acts on multiple innate and adaptive immune targets and can restore type 1 helper T (Th1)/Th2 balance. Sporadic studies have shown advances in pharmacology and therapeutics of OM-85, and thus an update review is necessary.
Methods: Literature was retrieved by searching PubMed, Web of science, Embase, CNKI, and Full Text Database of Chinese Medical Journals.
Abstract
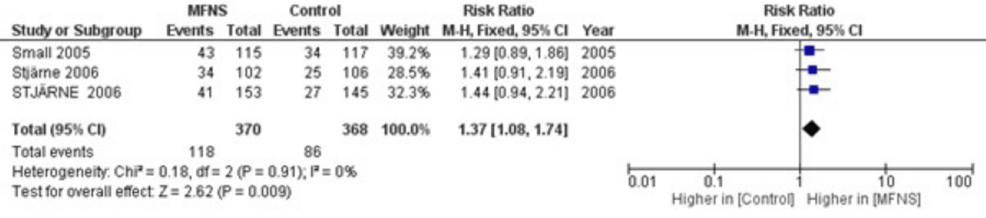 |
| Forest Plot of the Risk Ratio for Subjects With an
ImprovementWith MFNS Once Daily Compared to Placebo |