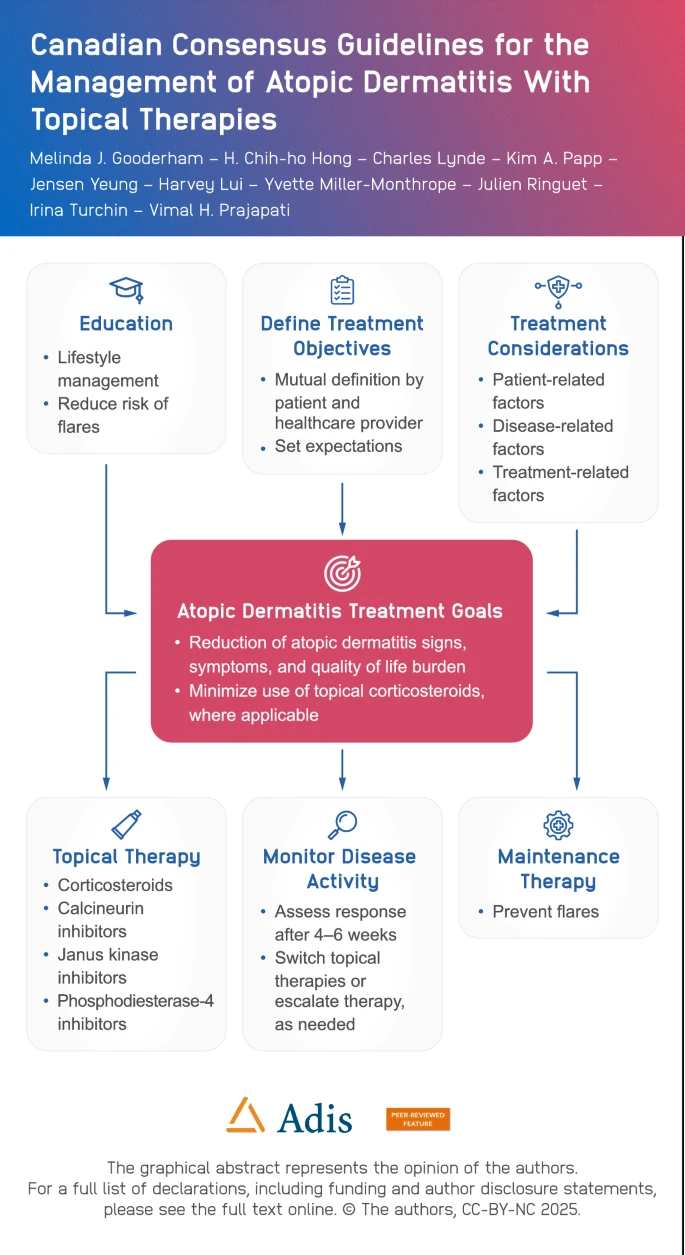
Abstract
Background
Anaphylaxis prevention and management in the school setting is an important health and safety issue as the rates of food allergy in children continue to increase.
Objective
We describe the development and review of the Australian National Allergy Council best practice guidelines for anaphylaxis prevention and management in schools.
Methods
Developed in consultation with key stakeholders in health and education settings, the best practice guidelines incorporate 7 key recommendations for anaphylaxis prevention and management: an allergy aware approach; anaphylaxis management policy and plans; allergy documentation; emergency response; staff training; community and student education; and postincident management and incident reporting.