 |
| The summary of pathogenesis and comparison between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. |
A blog that publishes updates and open access scientific papers about allergy, asthma and immunology. Editor: Juan Carlos Ivancevich, MD. Specialist in Allergy & Immunology
January 12, 2026
The molecular mechanism of the adverse effects of the biological and small molecular drugs in the therapy of inflammatory skin diseases - psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
January 9, 2026
Five-Grass-Pollen Sublingual Immunotherapy Drops Are Efficacious and Well Tolerated in Adults: The RHAPSODY Phase III Trial
Didier A, Juhl RG, Dalgaard T et al. Allergy. 2025 Dec 24. doi: 10.1111/all.70191.
ABSTRACT
Background
Tablet formulations of allergen extracts are widely recommended over other formulations for the sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) of respiratory allergies. However, with adequate clinical trial evidence, SLIT (liquid) drop formulations may be a relevant allergy treatment option.
Methods
 |
| Graphical Abstract |
Results
Of the 445 randomised patients (mean ± standard deviation (range) age: 32.6 ± 9.9 (18–63); males: 55.1%), 389 completed the trial.
January 8, 2026
Baseline Monocyte Count Predicts Complete Response to Omalizumab in Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: A Retrospective Analysis
Turhan İ D, Solak B (January 01, 2026) Cureus 18(1): e100556. doi:10.7759/cureus.100556
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a distressing skin condition characterized by wheals and angioedema. While omalizumab is an effective biologic therapy for antihistamine-refractory CSU, a subset of patients shows partial or no response. Identifying reliable biomarkers to predict treatment outcomes remains a significant clinical need. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between systemic inflammatory parameters, specifically monocyte counts, and the clinical response to omalizumab.
Methods: This retrospective study included 52 patients with CSU treated with omalizumab (300 mg/four weeks) for at least 12 weeks at a tertiary referral center. Patients were stratified into two groups based on their response at week 12: "Complete Response" (Urticaria Activity Score over seven days (UAS7) = 0) and "Non-Complete Response." Baseline and post-treatment complete blood count (CBC) parameters, C-reactive protein (CRP), and total IgE levels were analyzed. Binary logistic regression was performed to identify independent predictors of response.
 |
| Binary logistic regression analysis for independent predictors of complete response to omalizumab |
January 7, 2026
Rebound Pruritus and Urticaria Post-discontinuation of Chronic Cetirizine Use: A Case Report.
Seng J, Cai M, Oka P (December 27, 2025) Cureus 17(12): e100214. doi:10.7759/cureus.100214
Abstract
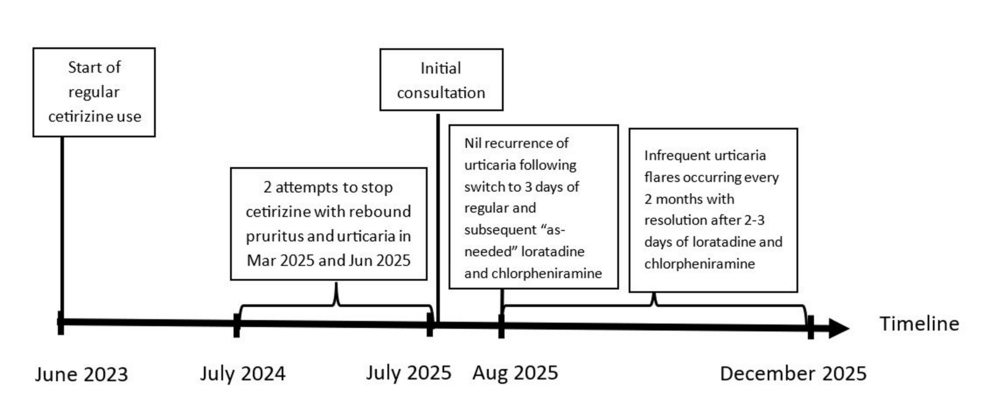 |
| Timeline of events |
Abstracts of the 14th C1-inhibitor Deficiency and Angioedema Workshop
Preface
We are pleased to welcome all participants to the 14th C1-inhibitor Deficiency & Angioedema Workshop.
The aim of the Workshop is to present new research findings related to rare bradykinin-mediated angioedema disorders. These include conditions caused by hereditary or acquired C1-inhibitor deficiency, as well as those with a hereditary background but normal C1-inhibitor levels. This year, a record number of abstracts will be presented over the four-day program, including 49 oral and 58 poster presentations. In addition to previously unpublished findings, five outstanding keynote lectures will also be delivered.
On the opening afternoon, Nobel Laureate Katalin Karikó will give a special lecture on the development of the mRNA vaccine, sharing all the insights gained from the long and persistent journey that led to the production of life-saving mRNA-based vaccines.
January 5, 2026
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination and 4-Year All-Cause Mortality Among Adults Aged 18 to 59 Years in France
Semenzato L, Le Vu S, Botton J, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(12):e2546822. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.4682
Question Are COVID-19 mRNA vaccines associated with the long-term risk of all-cause mortality?
Findings In this cohort study including 22.7 million vaccinated individuals and 5.9 million unvaccinated individuals, vaccinated individuals had a 74% lower risk of death from severe COVID-19 and no increased risk of all-cause mortality over a median follow-up of 45 months.
Meaning These national-level results found no increased risk of 4-year all-cause mortality in individuals aged 18 to 59 years vaccinated against COVID-19, further supporting the safety of the mRNA vaccines that are being widely used worldwide.
Importance While several studies have assessed the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on short-term mortality, none have compared long-term mortality by vaccination status, particularly in young individuals who are less likely to experience severe disease following SARS-CoV-2 infection.
January 3, 2026
TZ1391: a computationally designed circular mRNA multi-epitope vaccine candidate against Mycobacterium tuberculosis via TLR3 immunomodulation
Ali, A., Alamri, A., Mishra, V.K. et al. BMC Immunol (2026). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12865-025-00795-4
Abstract
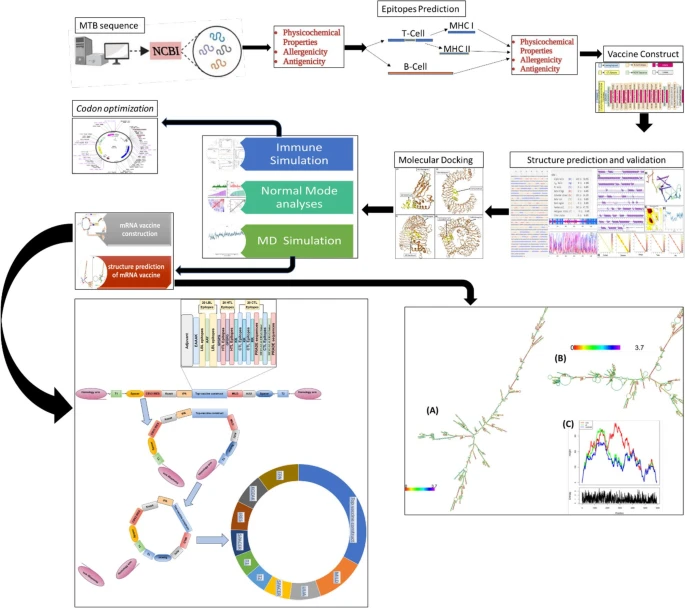 |
| Graphical Abstract |
January 2, 2026
Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Using 30 and 300 mg Maintenance Doses
 |
| Visual Summary |




