Abstract
Background
Previous studies have shown that IL-25 levels are increased in patients with asthma with fixed airflow limitation (FAL). However, the mechanism by which IL-25 contributes to airway remodeling and FAL remains unclear. Here, we hypothesized that IL-25 facilitates pro-fibrotic phenotypic changes in bronchial epithelial cells (BECs) and circulating fibrocytes (CFs), orchestrates pathological crosstalk from BECs to CFs, and thereby contributes to airway remodeling and FAL.
Methods
Fibrocytes from asthmatic patients with FAL and chronic asthma murine models were detected using flow cytometry, multiplex staining and multispectral imaging analysis.
The effect of IL-25 on BECs and CFs and on the crosstalk between BECs and CFs was determined using cell culture and co-culture systems.Results
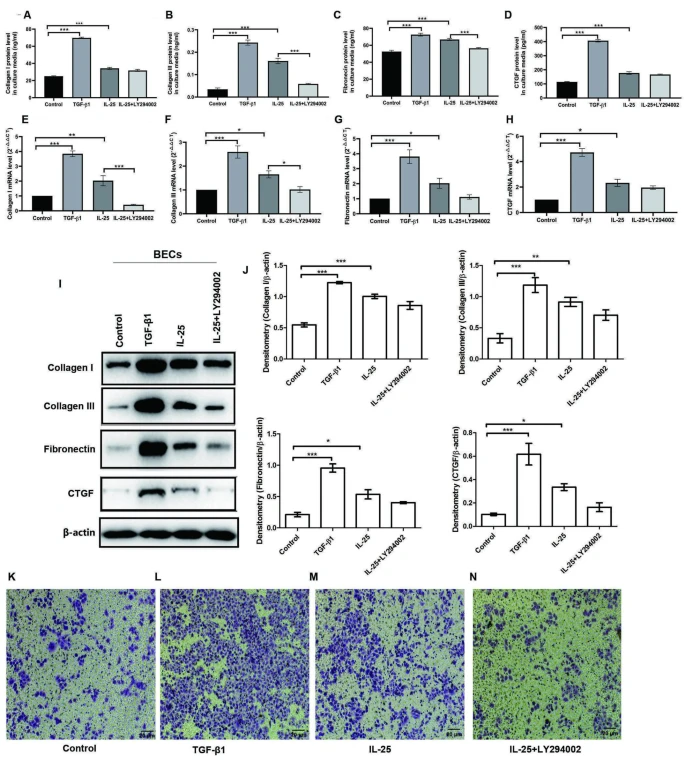 |
| IL-25 promotes pro-fibrotic phenotypic changes in BECs and was partially blocked with LY294002 |
Conclusion
These results suggest that IL-25 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for asthmatic patients with FAL.

No comments:
Post a Comment