Yasuda, M., Tobino, K., Harada, N. et al. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 20, 10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-024-00875-x
Abstract
Background
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs more commonly in asthma patients than in the general population because these conditions share some comorbidities. In Japan, the prevalence of OSA in the general population is reported to be approximately 20%; however, few reports have described the prevalence of OSA in asthma patients. Furthermore, the characteristics of Japanese patients with OSA and asthma are not clear.
Methods
Adult asthma patients were recruited from the outpatient departments of our institution between August 31, 2017, and March 31, 2019. In all included patients, the presence and severity of OSA were evaluated by the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) and a home sleep test (HST) using portable polysomnography (PSG). The rate of coexisting OSA in asthma patients and the characteristics of those patients according to the severity of OSA were investigated.
Results
Fifty-three patients were included. OSA was detected in 36 (67.9%) patients (mild, n = 15; moderate, n = 14; and severe, n = 7). Patients with OSA had significantly higher body mass index, Brinkman index, apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), and 3% oxygen desaturation index (ODI) values in comparison to those without OSA, while the percentage of the predicted value of forced vital capacity (%FVC) and lowest SpO2 levels were significantly lower. As the severity of OSA increased, age, brain natriuretic peptide level, AHI, and 3%ODI increased, and in contrast, FVC, %FVC, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), percentage of the predicted value of FEV1 (%FEV1), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS), 3%ODI, and lowest SpO2 levels decreased. In particular, the fact that the ESS value was inversely correlated with the severity of OSA in our patients was different from the general characteristics of OSA. Moreover, the AHI value was negatively correlated with FVC, %FVC, FEV1, and %FEV1. BMI was the only independent factor for the presence of OSA, and for asthma severity (FEV1, % of predicted), there was a weak correlation with smoking history.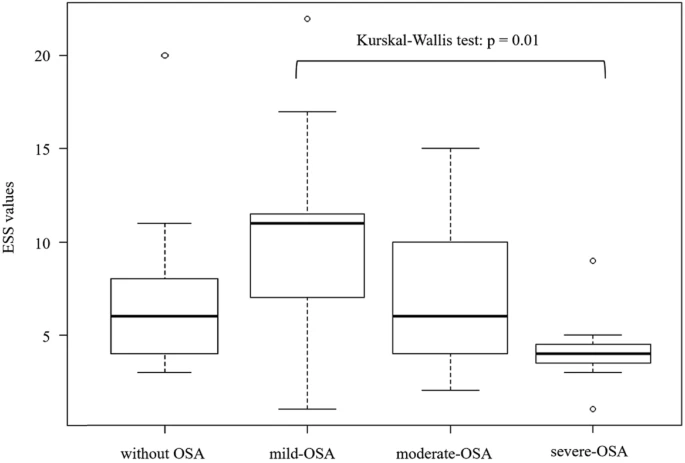
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) values according to
the severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Conclusions
This is the first report to investigate the prevalence of OSA in Japanese asthma patients, using an HST. This study suggests that an HST should be performed in addition to the sleep interview for asthma patients with refractory disease, a low pulmonary function, advanced age, and high BMI because the more severe the OSA, the lower the ESS value may be.

No comments:
Post a Comment