Tang R, Lyu X, Hou Y, Yang Y, Fu G, Zhu L, Xue L, Li H, Wang R. Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1363034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1363034.
Background: Hay fever, characterized by seasonal allergic reactions, poses a significant health challenge. Existing therapies encompass standard drug regimens, biological agents, and specific immunotherapy. This study aims to assess and compare the effectiveness of anti-IgE (omalizumab), medication therapy, and subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) for hay fever.
Methods: Conducted as a retrospective cohort study, this research involved 98 outpatient hay fever patients who underwent routine medication, omalizumab treatment, or SCIT before the onset of the spring pollen season. A follow-up was performed one month after the start of the pollen season. The comprehensive symptoms and drug scores were used to evaluate patients with different intervention methods, facilitating a comparative analysis of therapeutic outcomes.
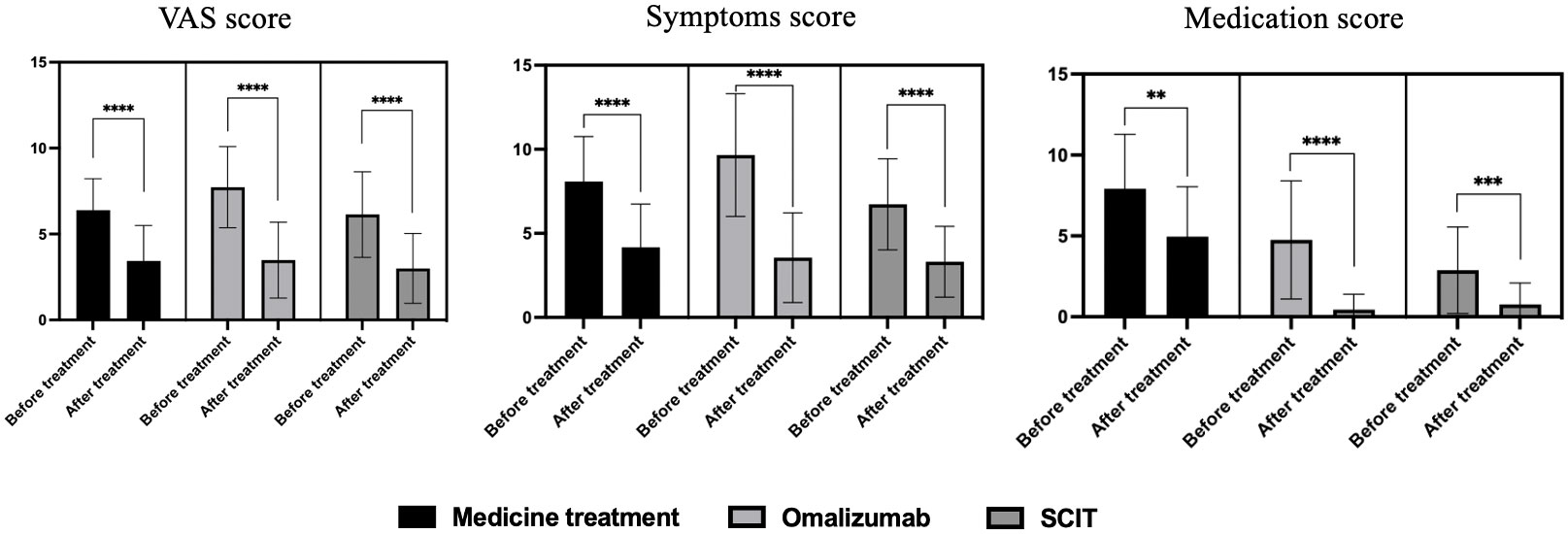 |
| VAS score, symptom score, and medication score before and after treatment of three therapies on hay fever patients. |
No comments:
Post a Comment