Puthumana, R.M., Grosgogeat, C.A., Davis, J.K. et al. BMC Pulm Med 24, 267 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-024-03066-x
Abstract
Background
Telemedicine use increased with the Covid-19 pandemic. The impact of telemedicine on resource use in pulmonary clinics is unknown.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study identified adults with pulmonary clinic visits at the University of Miami Hospital and Clinics (January 2018-December 2021). The primary exposure was telemedicine versus in-person visits. Standard statistics were used to describe the cohort and compare patients stratified by visit type. Multivariable logistic regression models evaluated the association of telemedicine with resource use (primarily, computed tomography [CT] orders placed within 7 days of visit).
Results
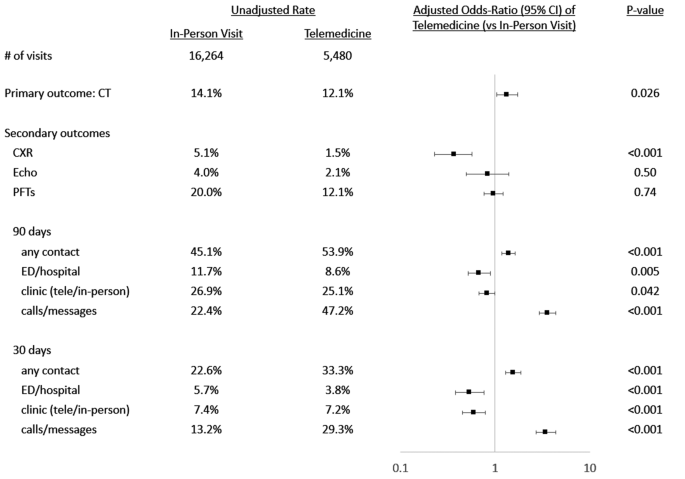 |
| Association of Telemedicine with Resource Use. |
Conclusions
Telemedicine was associated with an increased odds of chest CT order with a concomitant decreased odds of chest x-ray order. Increased contact with the healthcare system with telemedicine may represent a larger time burden for outpatient clinicians.

No comments:
Post a Comment