Balan, D., Baral, T., Manu, M.K. et al. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 20, 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-024-00922-7
Abstract
Background
Asthma is a chronic, heterogeneous disease characterized by airway inflammation. Asthma exacerbations significantly increase the disease burden, necessitating new therapeutic approaches. Emerging evidence suggests probiotics, through the gut-lung axis, may benefit asthma management by modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis adhered to PRISMA guidelines and was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023480098). A comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Embase was conducted up to March 2024. Inclusion criteria encompassed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating probiotic interventions in asthma patients. Statistical analysis was done using RevMan 5.3, with odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) calculated, and heterogeneity assessed using I2 statistics.
Results
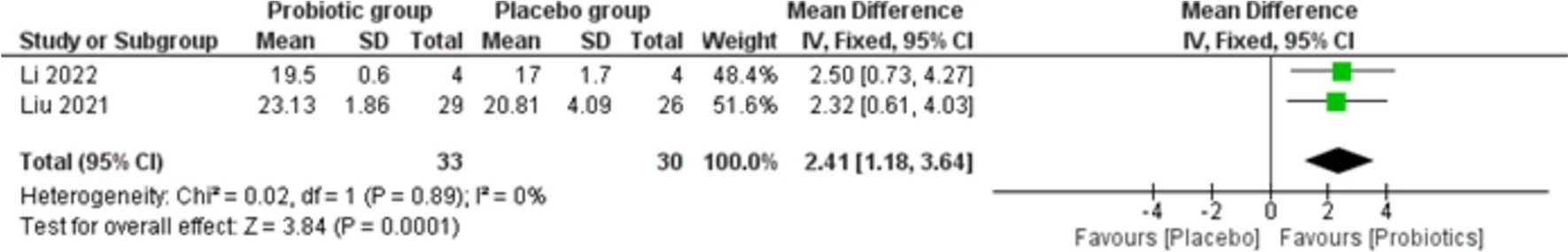 |
| Forest plot for asthma control test |
Conclusion
Probiotic supplementation may be beneficial in improving asthma symptom control with no significant impact on lung function indices or eosinophil levels. Probiotics can be a potential adjunctive therapy in asthma management, particularly for asthma symptom control.

No comments:
Post a Comment