Zhang, Y., Li, J., Wang, M. et al. Nat Med (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03651-5Abstract
Seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) places a significant socioeconomic burden, particularly on individuals with poorly managed recurrent and severe symptoms despite standard-of-care treatment. Stapokibart, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin (IL)-4 receptor subunit alpha, inhibits its interaction with both IL-4 and IL-13 in type 2 inflammation.
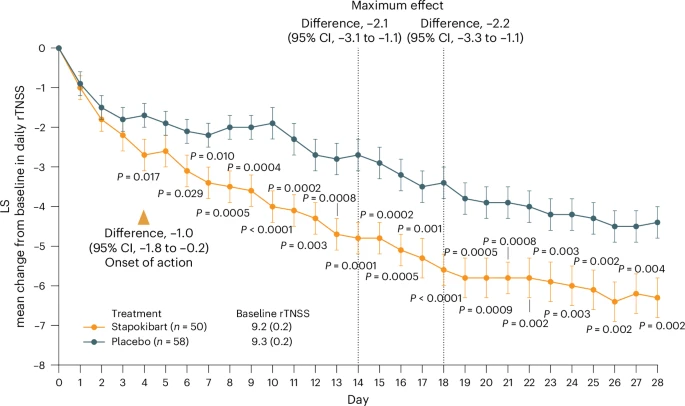 |
| Change from baseline over time in daily rTNSS during the 4-week treatment period. |
Here we aim to assess the efficacy and safety of stapokibart as an add-on therapy in adults with moderate-to-severe SAR. The study was a phase 3 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with 108 patients diagnosed with moderate-to-severe SAR and having baseline blood eosinophil counts ≥300 cells μl−1. Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive 600 mg (loading dose) to 300 mg stapokibart subcutaneously or a placebo every 2 weeks for 4 weeks. The primary endpoint was mean change from baseline in daily reflective total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) over the first 2 weeks. Multiplicity-tested secondary endpoints included changes in rTNSS over 4 weeks, reflective total ocular symptom score and Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire score over 2 weeks and 4 weeks. Compared with the placebo, stapokibart led to a significant improvement in the mean change from baseline in daily rTNSS during the 2-week (least-squares mean difference, −1.3; 95% confidence interval, −2.0 to −0.6; P = 0.0008) and 4-week (least-squares mean difference, −1.7; 95% confidence interval, −2.5 to −0.8; P = 0.0002) treatments. Stapokibart significantly improved the multiplicity-tested secondary endpoints. Treatment-emergent adverse events were comparable between the groups. Pharmacodynamics and exploratory analyses indicated that the observed improvements in outcomes during pollen season may be attributed to the reduction of type 2 inflammation in response to stapokibart treatment. The results of this trial show that pollen seasonal administration of stapokibart improved both nasal and ocular symptoms and quality of life in patients with moderate-to-severe SAR. PDF

No comments:
Post a Comment