Văruț RM, Dalia D, Radivojevic K, Trasca DM, Stoica GA, Adrian NS, Carmen NE, Singer CE. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;18(7):1021. doi: 10.3390/ph18071021.
Abstract
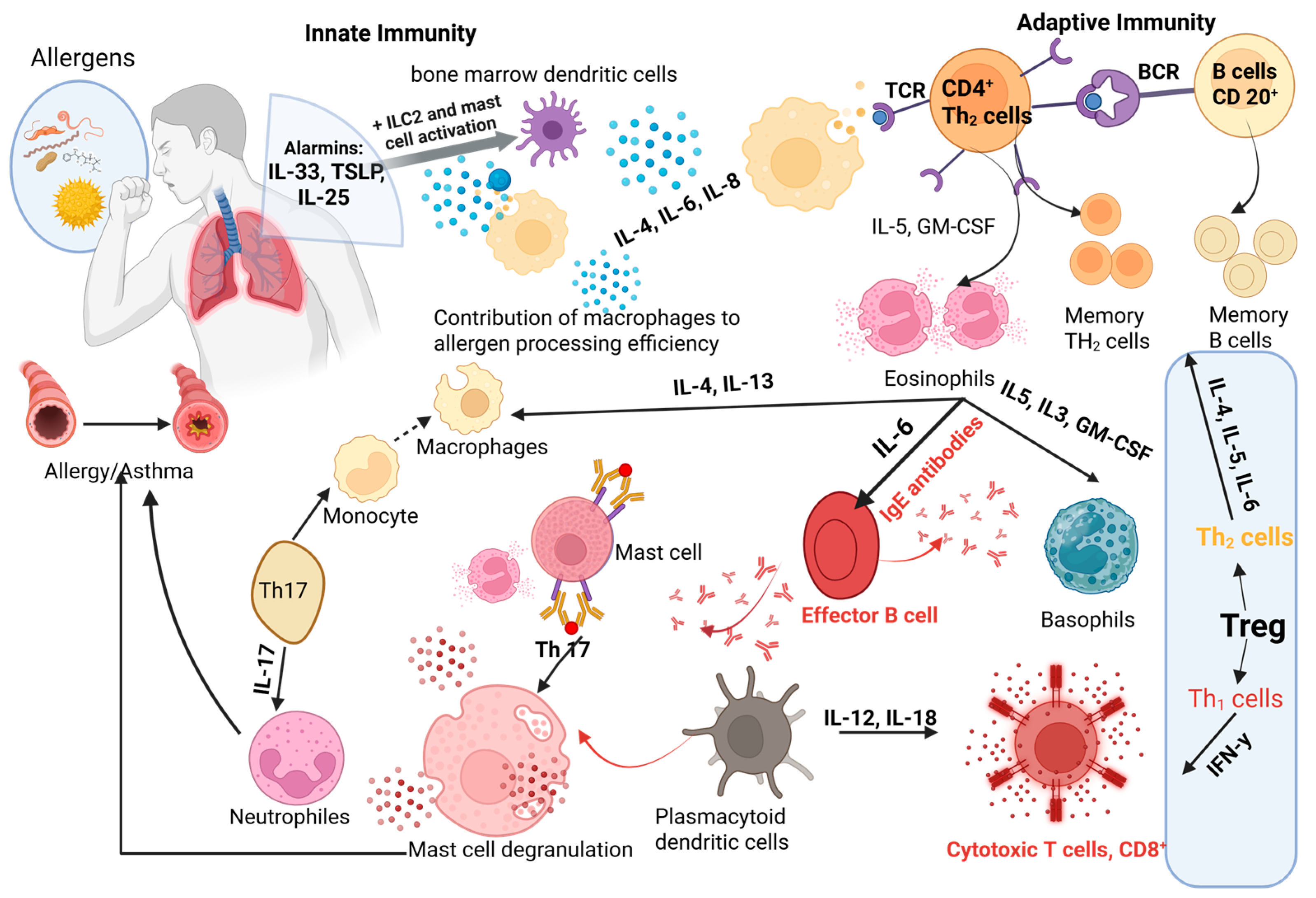 |
Immune cell differentiation and IgE-mediated responses
in allergic asthma pathogenesis |
Asthma represents a heterogeneous disorder characterized by a dynamic balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory forces, with allergic sensitization contributing substantially to airway hyperresponsiveness and remodeling. Central to its pathogenesis are cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-17, and IL-33, which drive recruitment of eosinophils, neutrophils, and other effector cells, thereby precipitating episodic exacerbations in response to viral and environmental triggers. Conventional biomarkers, including blood and sputum eosinophil counts, IgE levels, and fractional exhaled nitric oxide, facilitate phenotypic classification and guide the emerging biologic era. Monoclonal antibodies targeting IgE (omalizumab) and IL-5 (mepolizumab, benralizumab, reslizumab, depemokimab) have demonstrated the ability to reduce exacerbation frequency and improve lung function, with newer agents such as depemokimab offering extended dosing intervals. Itepekimab, an anti-IL-33 antibody, effectively engages its target and mitigates tissue eosinophilia, while CM310-stapokibart, tralokinumab, and lebrikizumab inhibit IL-4/IL-13 signaling with variable efficacy depending on patient biomarkers. Comparative analyses of these biologics, encompassing affinity, dosing regimens, and trial outcomes, underscore the imperative of personalized therapy to optimize disease control in severe asthma.PDF

No comments:
Post a Comment