Background
Recurrent use of oral corticosteroids (OCS) and over-use of short-acting beta-2-agonists (SABA) are factors associated with adverse side effects and asthma-related death. We aim to quantify high OCS exposure, SABA over-use and its association with prescription and adherence to maintenance treatment for respiratory disease, among patients with prescriptions for respiratory disease, from the Portuguese electronic prescription and dispensing database (BDNP).
Methods
This was a 1-year (2016) retrospective population-based analysis of a random sample of adult patients from the BDNP, the nationwide compulsory medication prescription system. We assessed high OCS exposure (dispensing ≥ 4 packages containing 20 doses of 20 mg each of prednisolone-equivalent, ≥ 1600 mg/year) on patients on persistent respiratory treatment (PRT-prescription for > 2 packages of any respiratory maintenance medications). Excessive use of SABA was defined as having a ratio of SABA-to-maintenance treatment > 1 or having SABA over-use (dispensing of > 1 × 200 dose canister/month, of 100 μg of salbutamol-equivalent). Factors associated with high OCS exposure were assessed by multinomial logistic regression.
Results
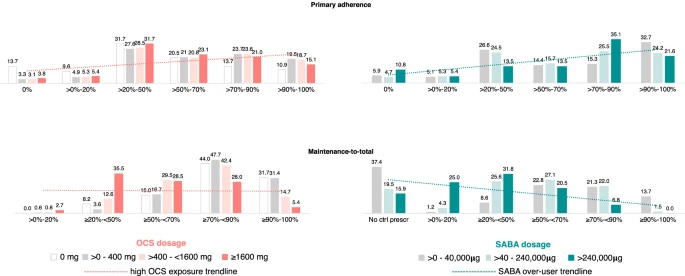 |
Frequency (%) of SABA users and OCS users on persistent respiratory treatment,
by primary adherence to controller medication and ratio maintenance-to-total |
The estimated number of patients on PRT was 4786/100,000 patients. OCS was prescribed to more than 1/5 of the patients on PRT and 101/100,000 were exposed to a high-dose (≥ 1600 mg/year). SABA excessive use was found in 144/100,000 patients and SABA over-use in 24/100,000. About 1/6 of SABA over-users were not prescribed any controller medication and 7% of them had a ratio maintenance-to-total ≥ 70% (high prescription of maintenance treatment). Primary adherence (median%) to controller medication was 66.7% for PRT patients, 59.6% for patients exposed to high OCS dose and 75.0% for SABA over-users. High OCS exposure or SABA over-use were not associated with primary adherence. High OCS exposure was associated with a maintenance-to-total medication ratio < 70% (insufficient prescription of maintenance treatment), age > 45 years old and male sex.
Conclusions
Exposure to high-dose of OCS (101 per 100,000 patients) and SABA over-use (24 per 100,000) were frequent, and were associated with a low maintenance-to-total prescription ratio but not with primary non-adherence. These results suggest there is a need for initiatives to reduce OCS and SABA inappropriate prescribing.