- Technical advance
- OPEN Open Peer Review
BMC Pulmonary Medicine
Mattis Gottlow,
David J. Svensson,
Ilya Lipkovich,
Monika Huhn,
Karin Bowen,
Peter Wessman &
Gene Colice
BMC Pulmonary Medicine
BMC Pulmonary Medicine 19, Article number: 129 (2019)
Abstract
Background
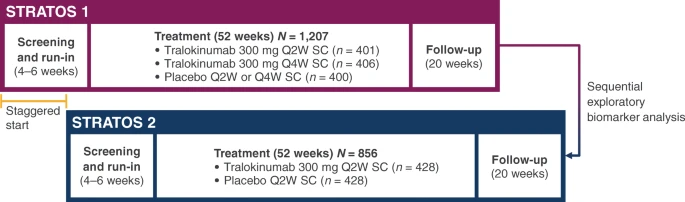 |
| Staggered trial design of STRATOS 1 and 2. Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks; SC, subcutaneous |
Tralokinumab is an anti–interleukin (IL)-13 monoclonal antibody investigated for the treatment of severe, uncontrolled asthma in two Phase III clinical trials, STRATOS 1 and 2. The STRATOS 1 biomarker analysis plan was developed to identify biomarker(s) indicative of IL-13 activation likely to predict tralokinumab efficacy and define a population in which there was an enhanced treatment effect; this defined population was then tested in STRATOS 2.