Introduction
Allergy to chicken egg protein is a common form of food allergy. The most common clinical presentation includes gastrointestinal, skin, and respiratory symptoms. Differential diagnosis, including provocative tests, is critical in diagnosis.
Case description
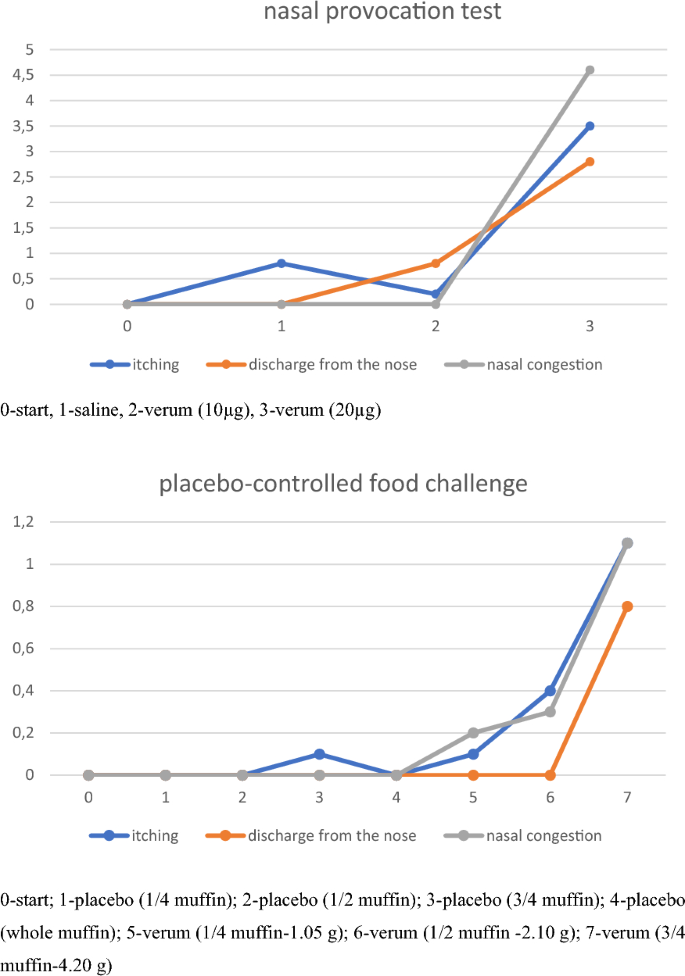
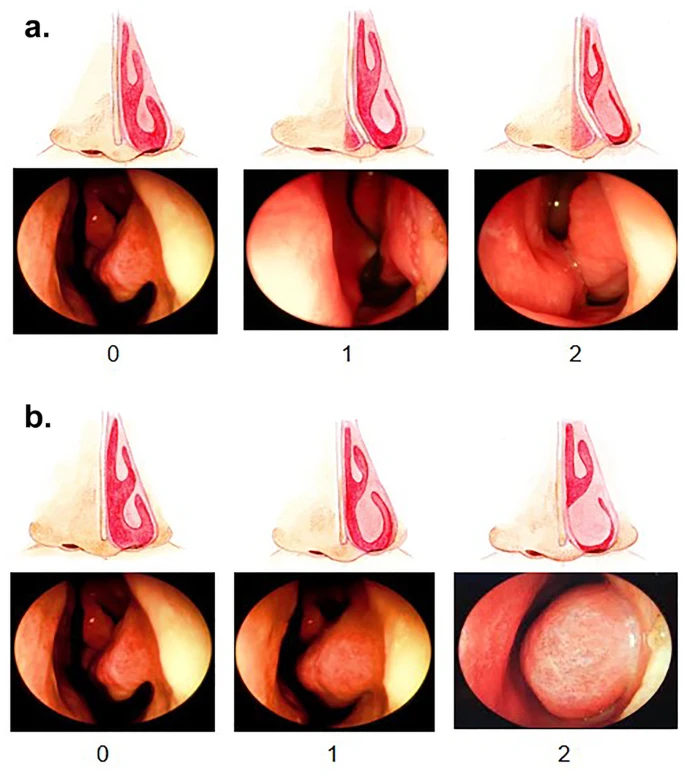
We present a case of a 21-year-old patient with egg allergy, who underwent a double-blind food provocation test with placebo (evaluating subjective complaints from the gastrointestinal tract) and a titrated nasal provocation test using dry chicken egg content. We assessed the response of the nasal mucosa in the provocation test using the visual analogue scale (VAS), acoustic and optical rhinometry, as well as measurements of nitric oxide concentration in the exhaled air. During the provocation test, we measured the changes in the transverse section of the nasal passages, which were accompanied by subjective complaints measured with the VAS scale, using objective techniques. In the nasal provocation test with a dose of 20 µg of chicken egg protein, we observed an increase in the reactivity of the nasal mucosa and a decrease in the level of nitric oxide in the exhaled air from the upper airways (920 ppb before the provocation test and up to 867 ppb during the early stage of the allergic reaction). During the provocation tests, we recorded typical symptoms associated with the early stage of the allergic reaction; including nasal obstruction (1.2 cm), leakage of watery discharge (0.8 cm) in the food test, and itchy nose (1.1 cm) in the food test vs. the nasal test: 4.6, 2.8, and 3.5 cm, respectively.
Conclusions
The nasal mucosa provides convenient conditions for evaluation of the severity of allergy to common food allergens, including chicken egg allergens.
PDF